Selective Breeding Drawing
Selective Breeding Drawing - Natural selection vs artificial selection video. The intentional breeding of organisms with desirable traits in an attempt to produce offspring with similar desirable characteristics or with improved traits. Web selective breeding involves selecting individuals of a species that have characteristics of interest in the hope that their offspring inherit those desirable characteristics. Read comprehension passages with vocabulary related to genetics and selective breeding. 5.10 understand how selective breeding can develop plants with desired characteristics Artificial selection is the process of selecting individuals with desired traits to produce offspring with those same traits. Punnet square practice this activity can be a companion to a secondary genetics lesson allowing students to practice completing punnett squares. Both selective (traditional) breeding and modern genetic engineering produce genetic modifications. Selective breeding handout, 1 copy per student. The traditional plant breeding process introduces a number of genes into the plant. Artificial selection and natural selection. Students will be able to. Genetic engineering allows for fewer and more precise genetic modifications. Natural selection vs artificial selection video. Read comprehension passages with vocabulary related to genetics and selective breeding. Animals can be selectively bred to take less development time before they enter the human food chain. Eventually, this process gives rise to new types of organisms. This is repeated over many generations. Both selective (traditional) breeding and modern genetic engineering produce genetic modifications. As opposed to natural selection, selective breeding focuses on traits which will benefit humans. Web artificial selection, or selective breeding, makes use of the principles of natural selection to create populations of animals or plants that align with the needs of human farmers, researchers or breeders of show or sporting animals. Web selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular. Web selective breeding is the process by which humans control the breeding of organisms in order to exhibit or eliminate a particular characteristic. How does selective breeding differ from genetic modification? Read comprehension passages with vocabulary related to genetics and selective breeding. As opposed to natural selection, selective breeding focuses on traits which will benefit humans. Selective breeding uses artificial. Both selective (traditional) breeding and modern genetic engineering produce genetic modifications. Artificial selection is the process of selecting individuals with desired traits to produce offspring with those same traits. Web principles of selective breeding programs. Worksheets and lesson ideas to challenge students aged 11 to 16 to think hard about selective breeding (gcse and key stage 3) selective breeding can. For selective breeding to be effective, there must be genetic variation present in the population, a way of identifying individuals for selection that are likely to transmit the desired properties to the descendants, and sufficient spare reproductive capacity so that the population can be bred from. Web selective breeding, the practice of mating individuals with desired traits as a means. Web another term for artificial selection is selective breeding. Bioengineering issues, solutions, and results. Differences in individual living things from each other. Students will be able to. The intentional breeding of organisms with desirable traits in an attempt to produce offspring with similar desirable characteristics or with improved traits. Artificial selection is the process of selecting individuals with desired traits to produce offspring with those same traits. This is repeated over many generations. Artificial selection and natural selection. Selective breeding of tobacco plants. Web selective breeding is the process by which humans control the breeding of organisms in order to exhibit or eliminate a particular characteristic. Selective breeding of tobacco plants. Genetics, trait, drought, meiosis, genetic modification, strong root system, rootworm resistance, seedling disease resistance. Punnet square practice this activity can be a companion to a secondary genetics lesson allowing students to practice completing punnett squares. Worksheets and lesson ideas to challenge students aged 11 to 16 to think hard about selective breeding (gcse and key. As opposed to natural selection, selective breeding focuses on traits which will benefit humans. Green leaves ( g) and white leaves ( g). Selective breeding can replicate what gmo work provides. Crops can be selectively bred to bring a yield to harvest in a faster time. Punnet square practice this activity can be a companion to a secondary genetics lesson. Students will be able to. Web selective breeding is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females. Web selective breeding involves selecting individuals of a species that have characteristics of interest in the hope that their offspring inherit those desirable characteristics. Recipe cards (1 recipe per group) a recipe for dna image. What are the advantages of selective breeding? Eventually, this process gives rise to new types of organisms. Differences in individual living things from each other. Selective breeding handout, 1 copy per student. Punnet square practice this activity can be a companion to a secondary genetics lesson allowing students to practice completing punnett squares. Web selective breeding is the process by which humans control the breeding of organisms in order to exhibit or eliminate a particular characteristic. Genetic engineering allows for fewer and more precise genetic modifications. Selective breeding of tobacco plants. Natural selection vs artificial selection video. Both selective (traditional) breeding and modern genetic engineering produce genetic modifications. Web another term for artificial selection is selective breeding. During artificial selection, humans choose parent organisms with specific traits and allow them to reproduce.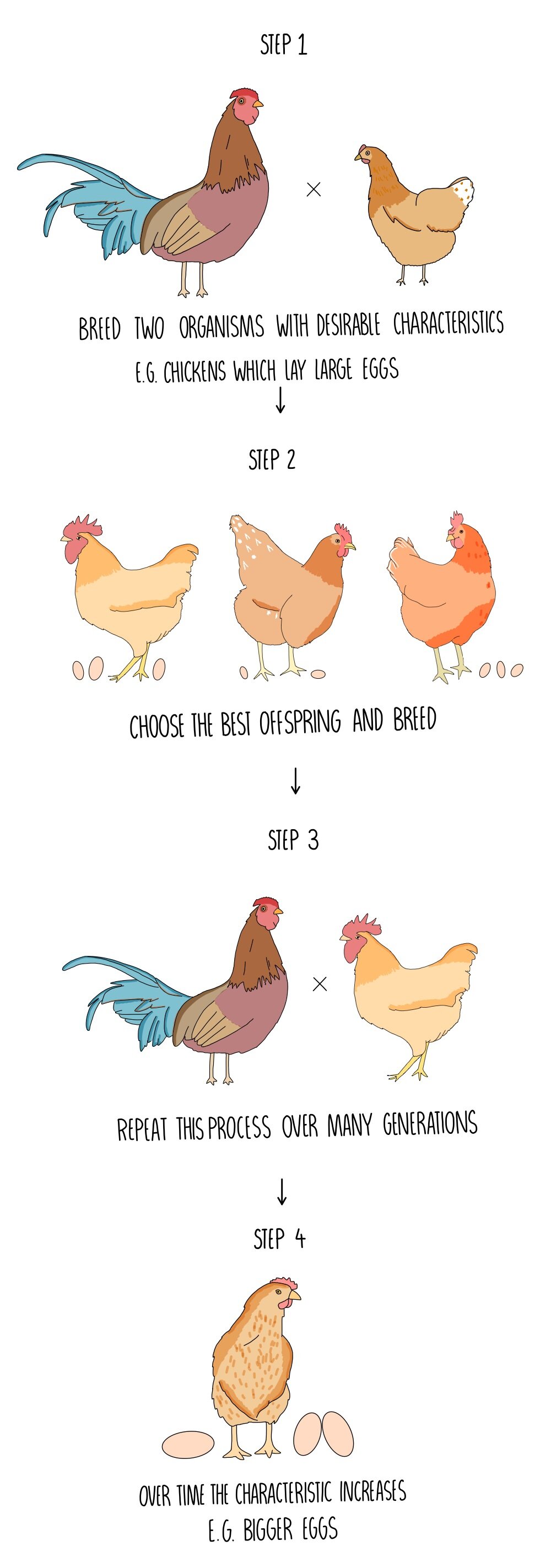
Selective breeding (GCSE) — the science hive
Selective Breeding Cloning Lessons Blendspace
Variation and Selective Breeding (GCSE Biology AQA) Teaching Resources
Variation and Selective Breeding (GCSE Biology AQA) Teaching Resources
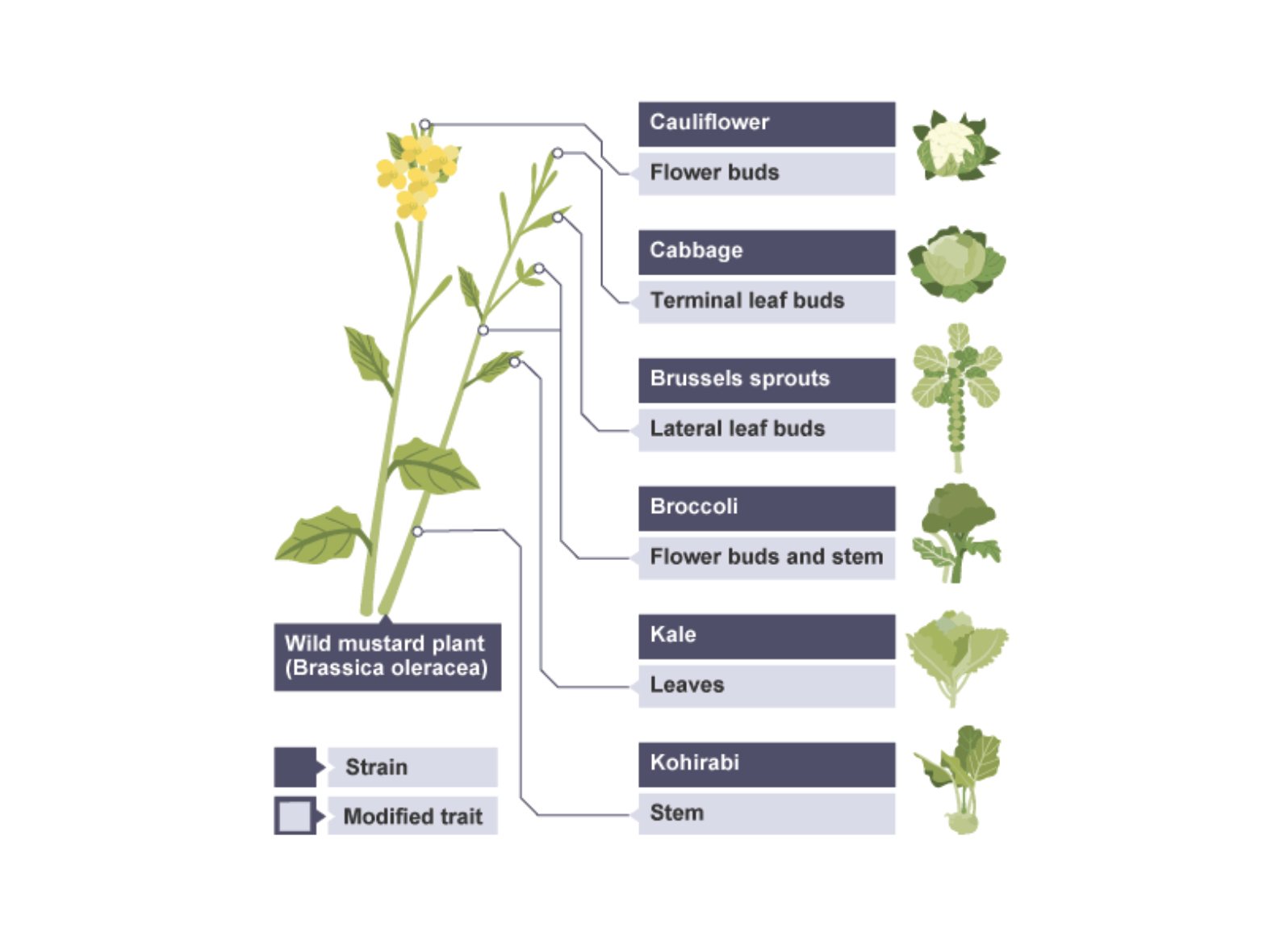
IGCSE Biology 2017 5.10 Understand that Plants with Desired

Selective Breeding How Farmers make Food Better ClimateScience

What is selective breeding? Facts
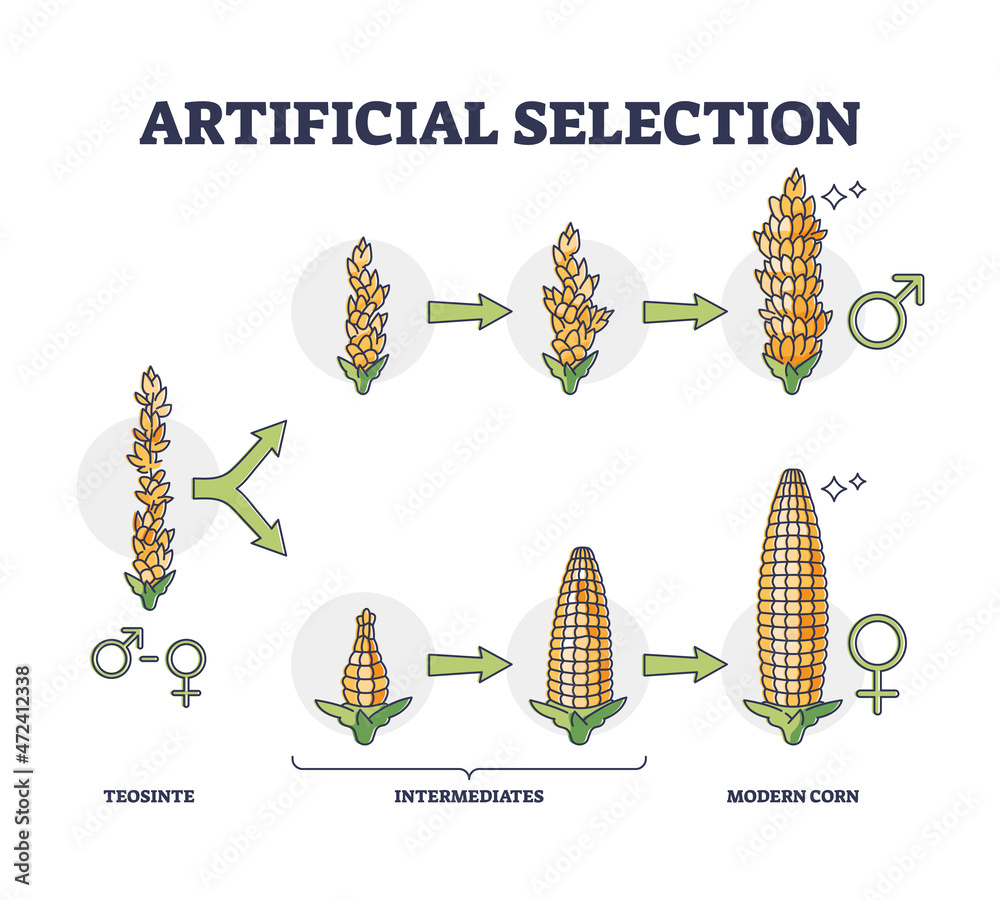
Artificial selection with selective breeding for vegetables outline
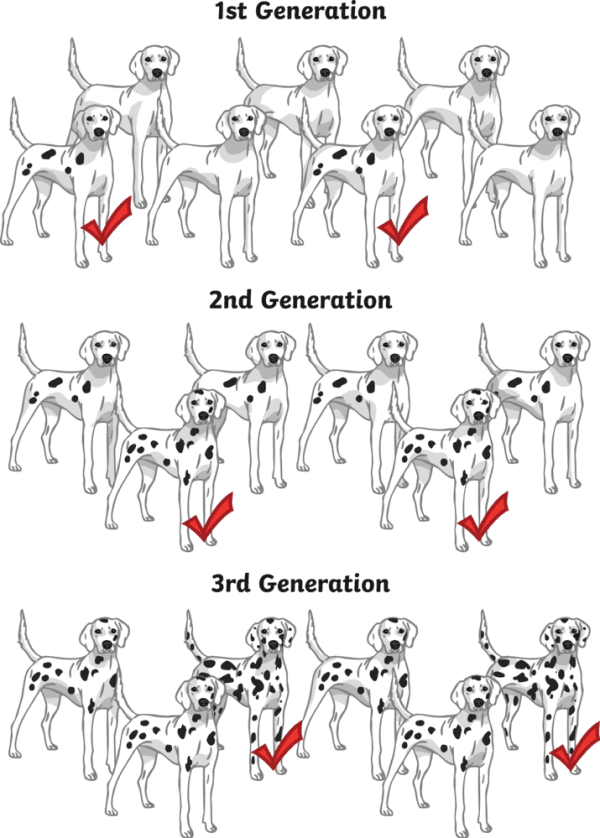
What is Selective Breeding? Twinkl NZ Twinkl

PPT 4 .3 Selective Breeding PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The Intentional Breeding Of Organisms With Desirable Traits In An Attempt To Produce Offspring With Similar Desirable Characteristics Or With Improved Traits.
Web Selective Breeding (Also Called Artificial Selection) Is The Process By Which Humans Use Animal Breeding And Plant Breeding To Selectively Develop Particular Phenotypic Traits (Characteristics) By Choosing Which Typically Animal Or Plant Males And Females Will Sexually Reproduce And Have Offspring Together.
Bioengineering Issues, Solutions, And Results.
For Selective Breeding To Be Effective, There Must Be Genetic Variation Present In The Population, A Way Of Identifying Individuals For Selection That Are Likely To Transmit The Desired Properties To The Descendants, And Sufficient Spare Reproductive Capacity So That The Population Can Be Bred From.
Related Post:

