Which Strand Is The Template Strand
Which Strand Is The Template Strand - During transcription, rna polymerase reads the template strand from 3′ to 5′. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Rna polymerase does not read the coding strand during transcription. In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web the coding strand moves from 5′ to 3′ along the dna molecule. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. This template strand. During transcription, rna polymerase reads the template strand from 3′ to 5′. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The template strand moves in the opposite direction, from 3′ to 5′. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web the coding strand moves from 5′ to 3′ along the dna molecule. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. During transcription, rna polymerase reads the template strand from 3′. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Web each strand of dna acts as. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that Web the coding strand moves from 5′ to 3′ along the dna molecule. During transcription, rna polymerase reads. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical. Rna polymerase does not read the coding strand during transcription. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t). Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called. Rna polymerase does not read the coding strand during transcription. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web the coding strand moves from 5′ to 3′ along the dna molecule. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Web the coding strand moves from 5′ to 3′ along the dna molecule. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. During transcription, rna polymerase reads the template strand from 3′ to 5′. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up.
Non Template Dna Strand

Template Strand Mrna

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
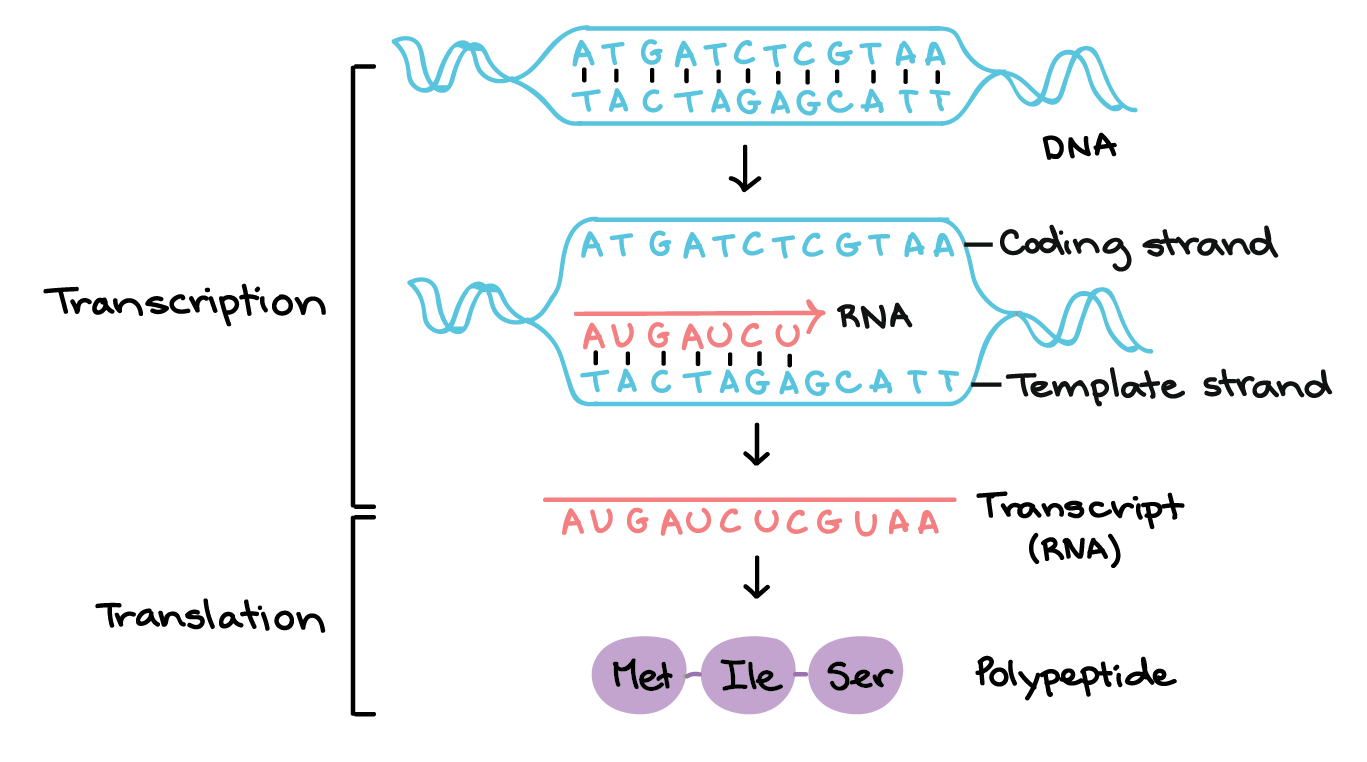
Protein Synthesis DNA Transcription, DNA Translation Gene

Coding Versus Template Strand

Indicate The Sequence Of The Template Strand Printable Word Searches

Answered Template strand New strand New strand… bartleby
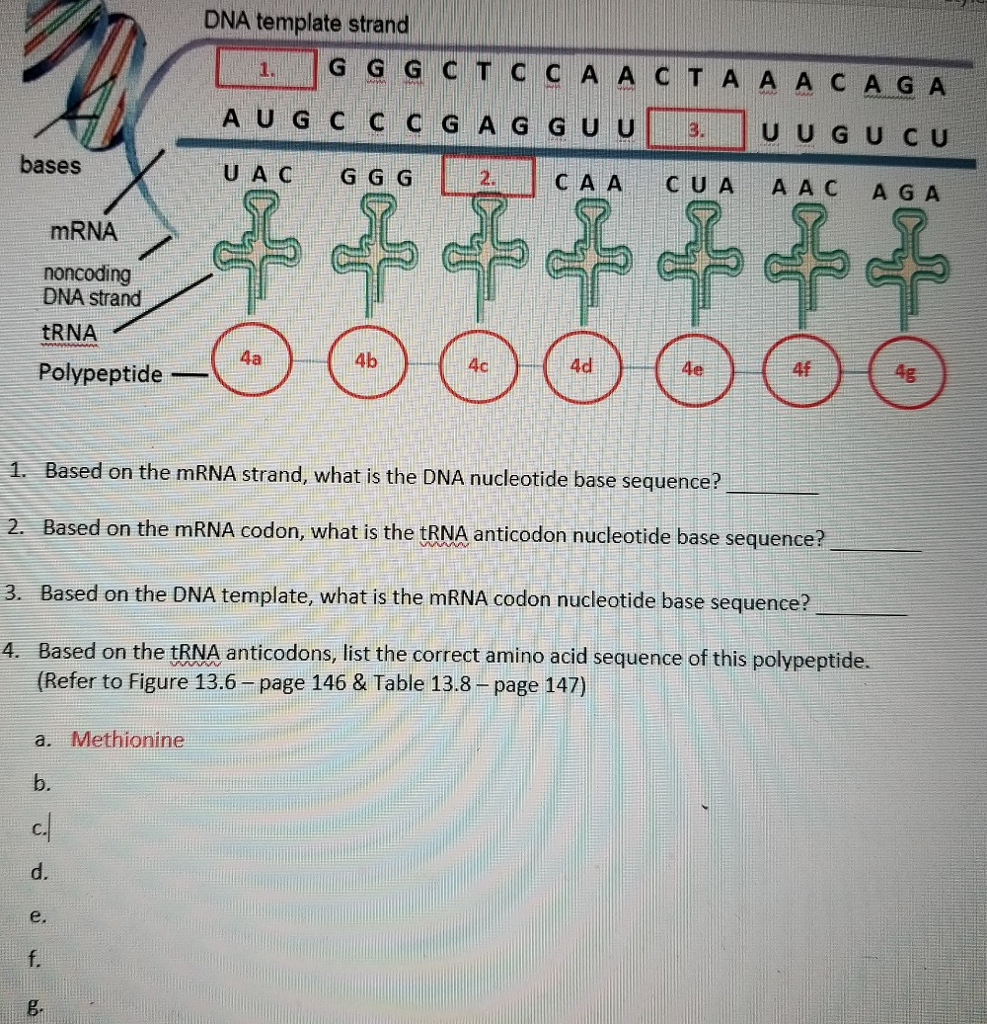
Mrna Template Strand

Difference Between Coding Strand And Template Strand
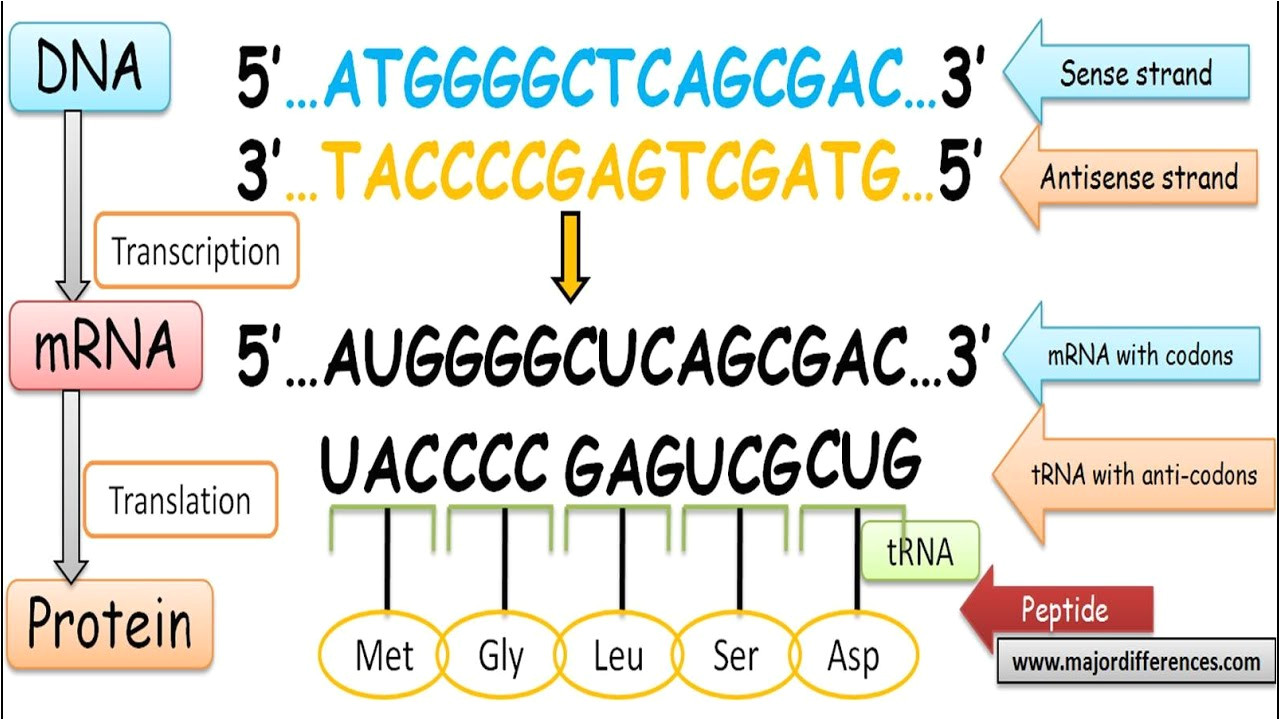
Coding Versus Template Strand
The Template Strand Moves In The Opposite Direction, From 3′ To 5′.
Rna Polymerase Does Not Read The Coding Strand During Transcription.
Web Each Strand Of Dna Acts As A Template For Synthesis Of A New, Complementary Strand.
In Conservative Replication, The Parental Dna Is Conserved, And The Daughter Dna Is Newly Synthesized.
Related Post: