Template Vs Non Template Strand
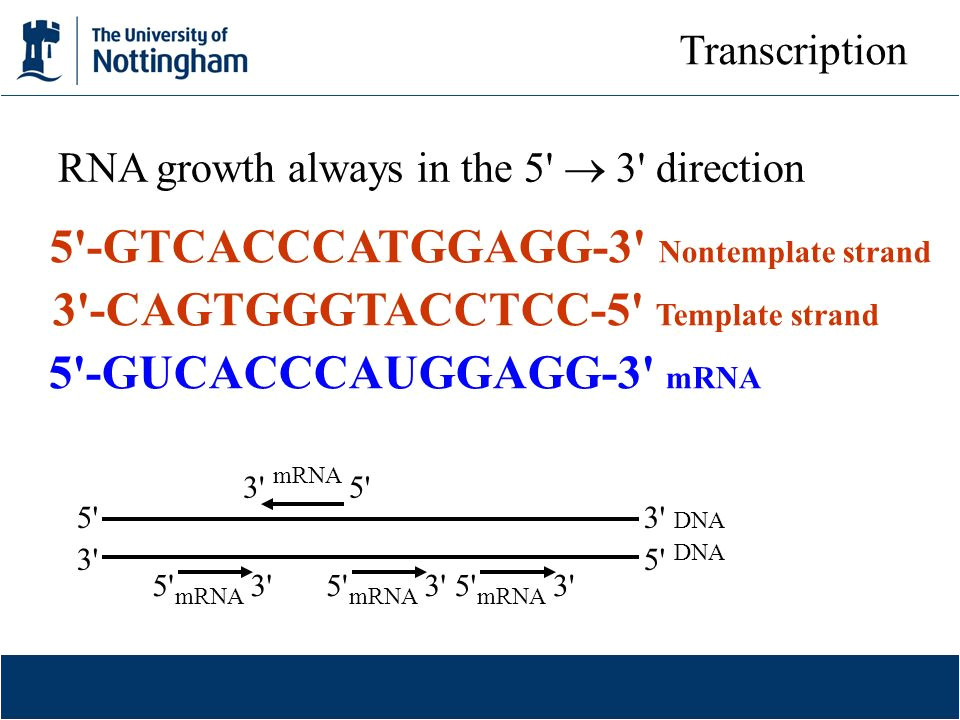
Template Vs Non Template Strand - This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′. Therefore, the main difference between template and coding strand is their ability to be transcribed by rna polymerases. Core enzyme (synthesizes rna) sigma factor (determines where/when to synthesize) what are the 3 phases of transcription? After binding to the promoter, repeated cycles of initiation and product release result in the accumulation of short abortive products. These two strands work together in a dynamic relationship. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. Transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand. It is complementary to the coding strand and is often referred to as the antisense strand. The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Core enzyme (synthesizes rna) sigma factor (determines where/when to synthesize) what are the 3 phases of transcription? Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ),. It can make a copy of itself during mrna synthesis. 37k views 3 years ago. Web the answer is simple : Rna polymerase reads the template strand to make mrna. Transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; After binding to the promoter, repeated cycles of initiation and product release result in the accumulation of short abortive products. This strand is read by rna polymerase from 3′ to 5′. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. The dna double helix then unwinds, and rna synthesis begins at the start point on the template strand. The term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. After binding to the promoter, repeated cycles of initiation and product release result in the accumulation of short abortive products. It is complementary to the coding strand and is often referred to as the antisense strand. The coding strand of dna is the strand. The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. Rna polymerase reads the template strand to make mrna. The coding strand does not read, but it has the same sequence as mrna. The term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. It can make a copy of itself during mrna synthesis. This strand is also called the coding. It is complementary to the coding strand and is often referred to as the antisense strand. The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand. The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. Web ssb hotspots around tsss are enriched on the template strand and associate with higher expression of the corresponding genes. The coding strand does not read, but it has the same sequence as mrna. The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act. These two strands work together in a dynamic relationship. Rna polymerase reads the template strand to make mrna. The term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. The coding strand does not read, but it has the same sequence as mrna. Web ssb hotspots around tsss are enriched on the template strand and. It is complementary to the coding strand and has a sequence that is identical to the rna transcript, except for the substitution of thymine with uracil in rna. Web wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3]. The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Web the template strand, on the other hand, is like the builder’s scaffold, providing a template for the synthesis of a new dna strand. Web ssb hotspots around tsss are enriched on the template strand and. The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. The template strand is complementary to. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. Transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; During transcription, one of the two. Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Web rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. Core enzyme (synthesizes rna) sigma factor (determines where/when to synthesize) what are the 3 phases of transcription? Write the similarities between the template and coding strand. The coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. The coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. The dna double helix then unwinds, and rna synthesis begins at the start point on the template strand of dna. Web the answer is simple : These two strands work together in a dynamic relationship. Web ssb hotspots around tsss are enriched on the template strand and associate with higher expression of the corresponding genes.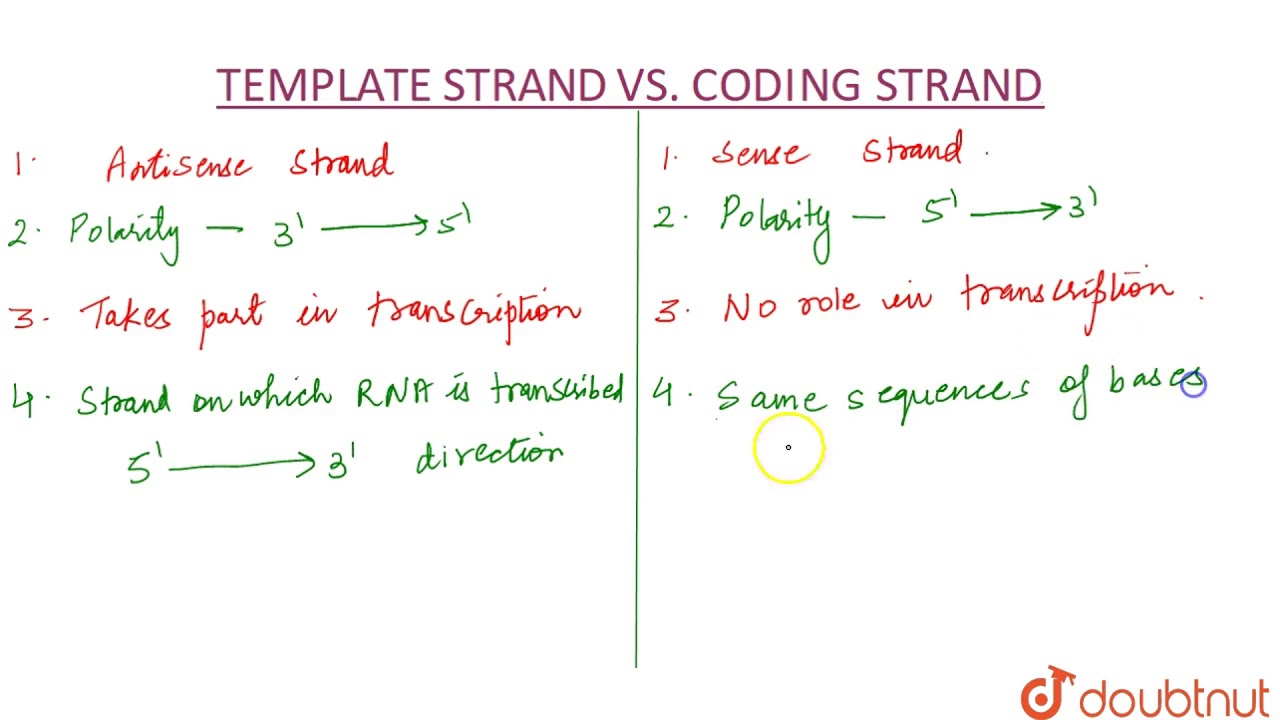
Difference Between Template And Coding Strand
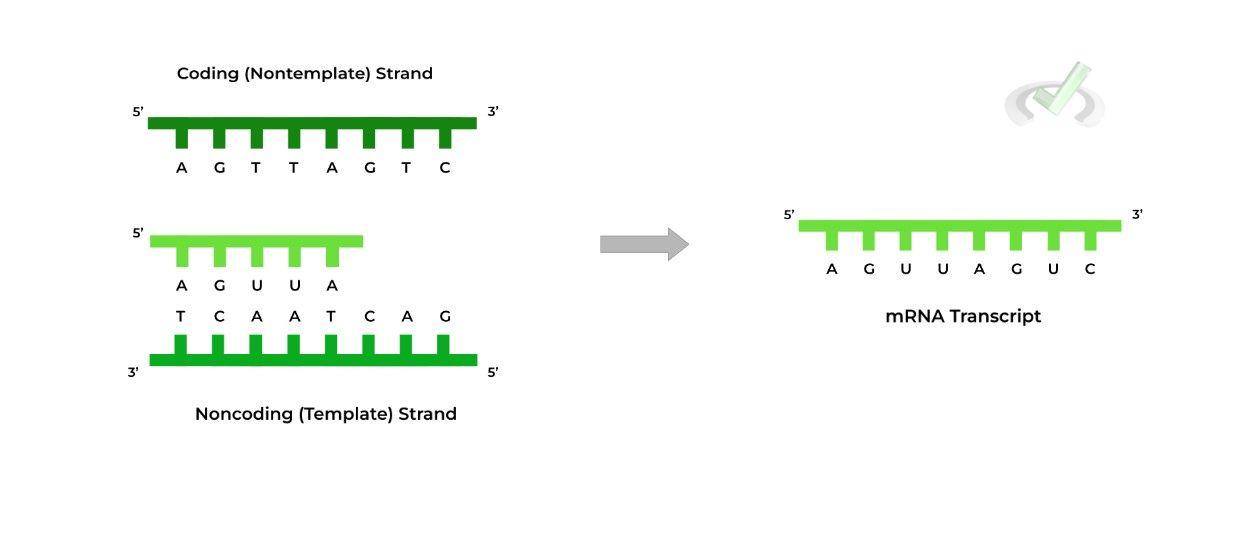
Template And Nontemplate Strand

Template Vs Nontemplate Strand
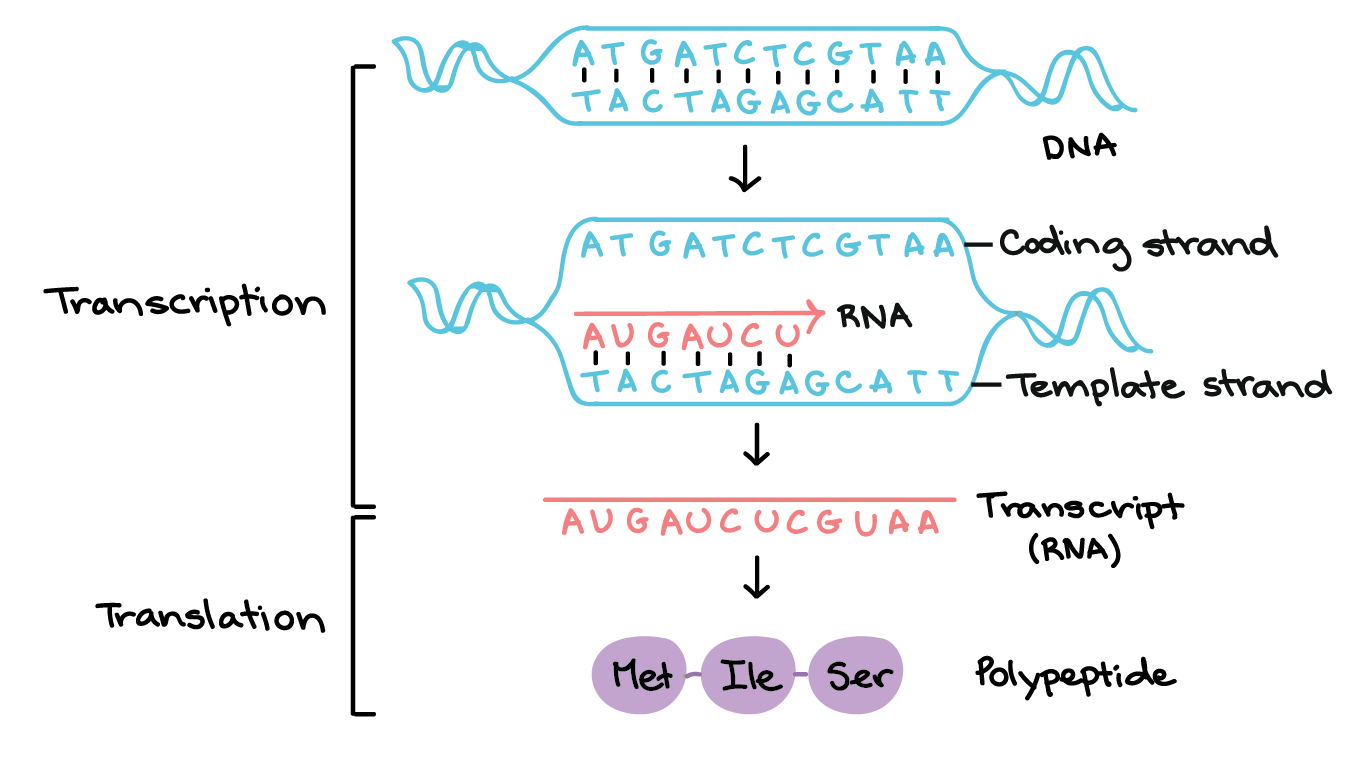
The Template For Rna Synthesis
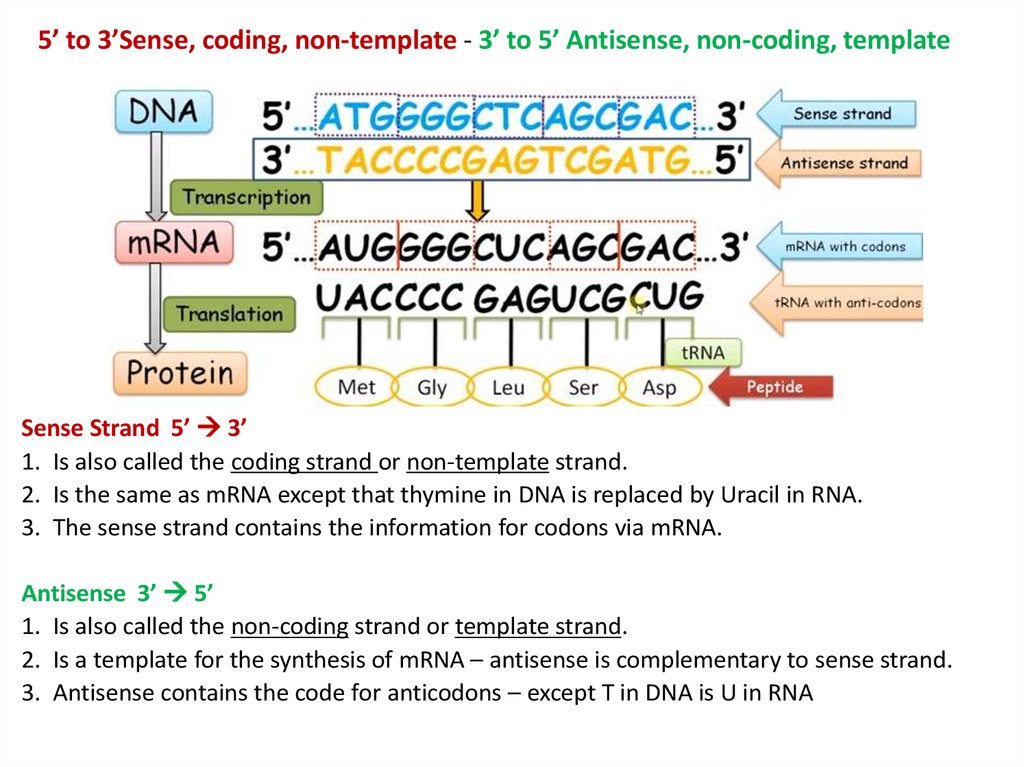
Transcription and Translation and the Code online presentation

Coding Versus Template Strand During Transcription, Only One Of The Two
What is the Template Strand williamsonga.us

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Variations sciencesavers

Template Strand Mrna

Non Template Dna Strand
Web 3) Additional Transcription Factors Bind To The Dna Along W/ Rna Polymerase Ii, Forming The Transcription Initiation Complex.
This Strand Is Read By Rna Polymerase From 3′ To 5′.
Web The Template Strand, On The Other Hand, Is Like The Builder’s Scaffold, Providing A Template For The Synthesis Of A New Dna Strand.
It Can Make A Copy Of Itself During Mrna Synthesis.
Related Post: