Template In Dna
Template In Dna - Web either dna strand can be a template. The rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the second function of dna (the first was replication) is to provide the information needed to construct the proteins necessary so that the cell can perform all of. The double helix is un'zipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Web dna template translation is the process of using an mrna molecule as a template to produce a protein. Concepts in biology (openstax) 9: Web coding strand vs. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web rna is also used as a template for creating proteins. Web during dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. Web like dna replication in an organism, pcr requires a dna polymerase enzyme that makes new strands of dna, using existing strands as templates. What is dna template strand? Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the. Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Smaller and more mobile than the dna sequence that it. The double helix is un'zipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Think of an mrna transcript as a portable gene: Dna is the information molecule. So, the coding strand and template strand are the two complementary strands forming the double helix structure of dna, and they play crucial. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. Web the transformation of the dna template in rna polymerase. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Concepts in biology (openstax) 9: So, the coding strand and template strand are the two complementary strands forming the double helix structure of dna, and they play. Incubation, vortexing, washing, elution, use of controls). A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into. The replication of dna occurs during the synthesis phase, or s phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the dna. So, the coding strand and template strand are the two complementary strands forming the double helix structure of dna,. Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together (. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The double helix is un'zipped' and unwound, then each separated strand (turquoise) acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand (green). Web an mrna transcript is a single strand of rna that encapsulate the information. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. Web rna is also used as a template for creating proteins. Nucleotides (bases) are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices. This is accomplished by the process of dna replication. Web either dna strand can be a template. Major types of cellular rna. Identify the key steps of transcription, the function of the promoter and the function of rna polymerase. Web a dna molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. Smaller and more mobile than the dna sequence that it is built from, but containing the same information. This is accomplished. Web either dna strand can be a template. What does an mrna transcript look like? What is dna template strand? Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together (. Web rna is also used as a template for creating proteins. Please specify the actions you took to extract the dna from your samples and note what equipment was used to do so (e.g. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. So, the coding strand and template strand are the two complementary strands forming the double helix structure of dna, and they play crucial roles in processes like transcription and translation, which are essential for protein synthesis. Mrna, a scrupulous rna copy of the ‘coding’ strand of dna (also known as ‘sense’ or ‘plus’ strand), is translated into amino acid polymers (polypeptides) by the ribosomal machinery. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the dna. Major types of cellular rna. Web coding strand vs. Guide to research techniques in neuroscience (third edition) , 2022
19.3 Replication and Expression of Information The Basics of

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

replication Britannica
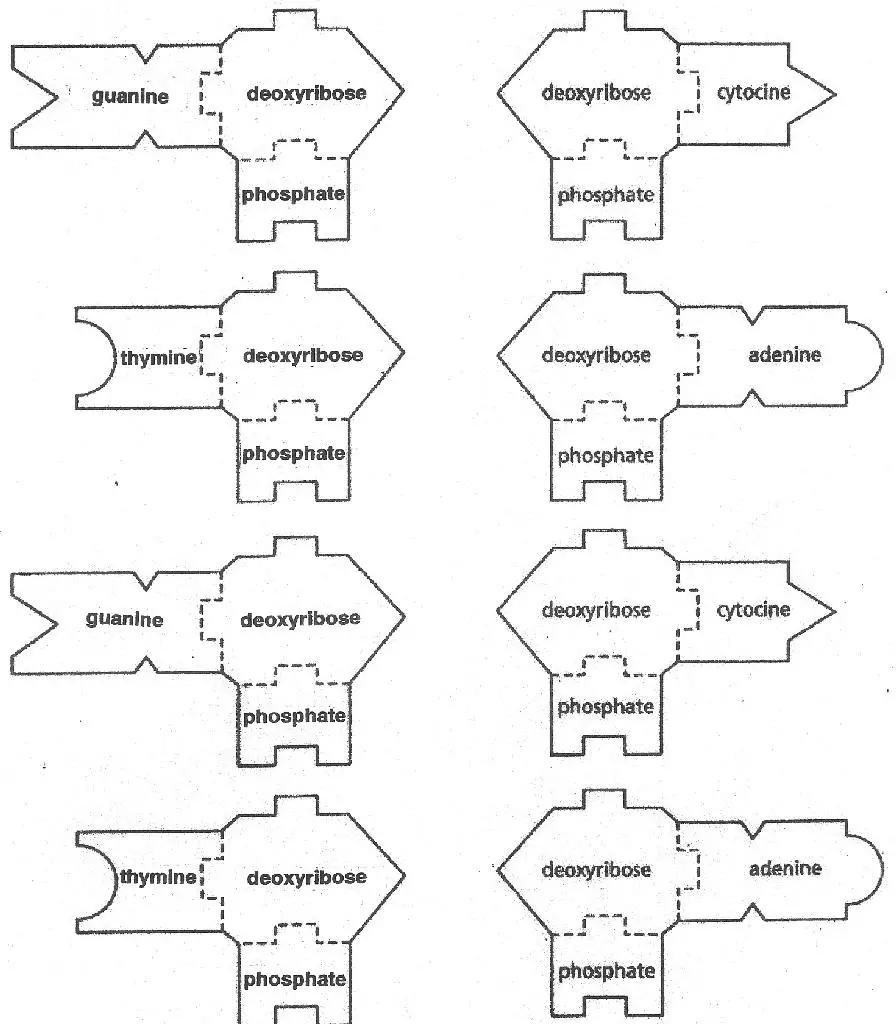
DNA & RNA Templates Science Classroom Teacher Resources

DNA Template DNA PowerPoint Template

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA PowerPoint Template for Presentation & Google Slides
The Nontemplate Strand Is Referred.
Web Rna Polymerase Binds To A Sequence Of Dna Called The Promoter, Found Near The Beginning Of A Gene.
Concepts In Biology (Openstax) 9:
These Enzymes Utilize Energy From Atp To Move On Dna, Destabilize The Hydrogen Bonds Between Bases, And Separate The Two Strands Of The Double Helix.
Related Post: