Template And Coding Strand
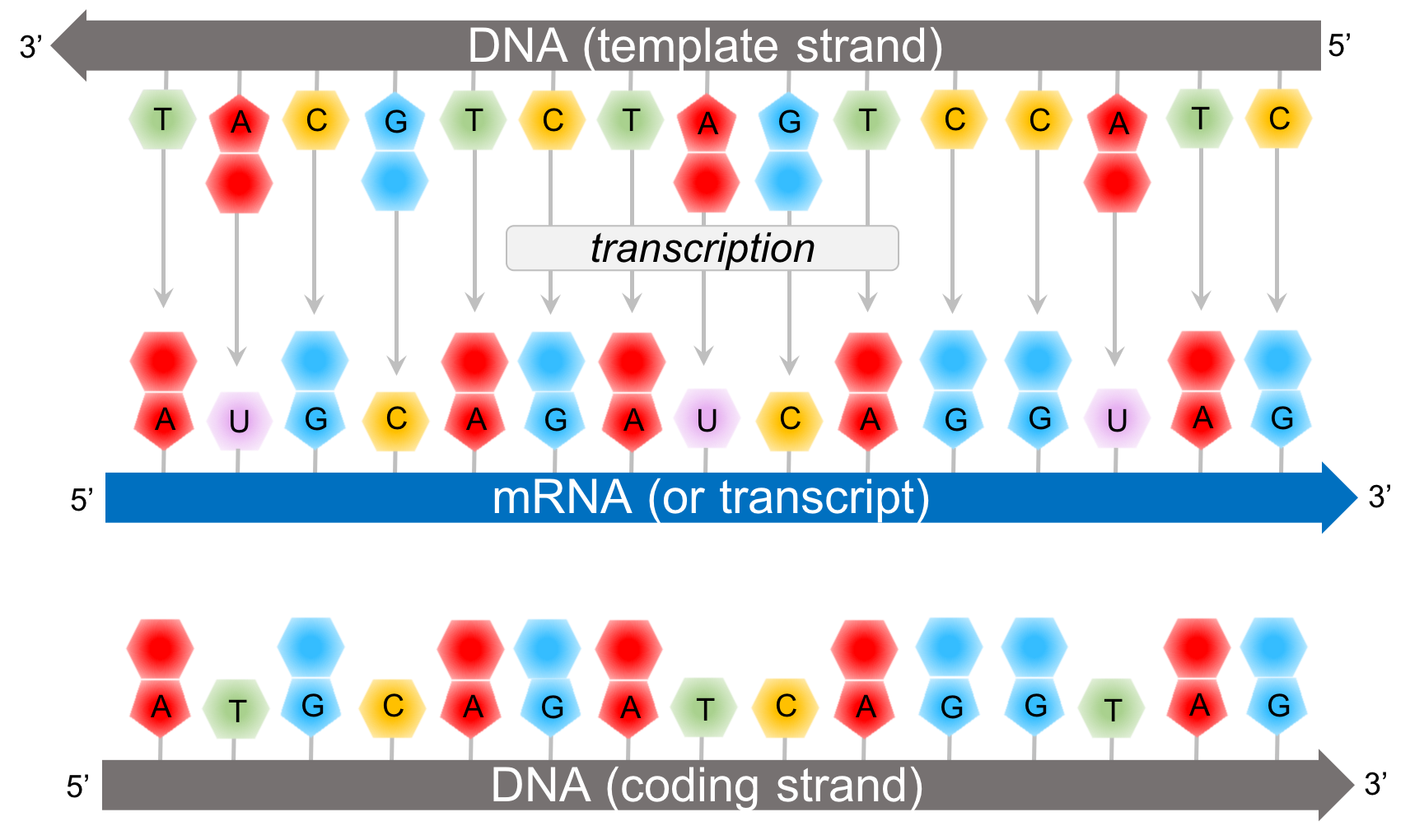
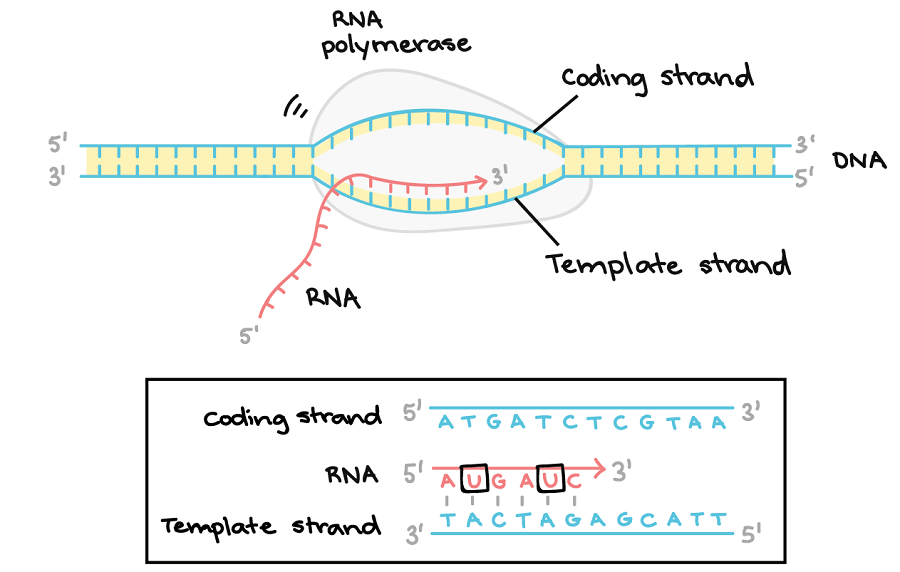
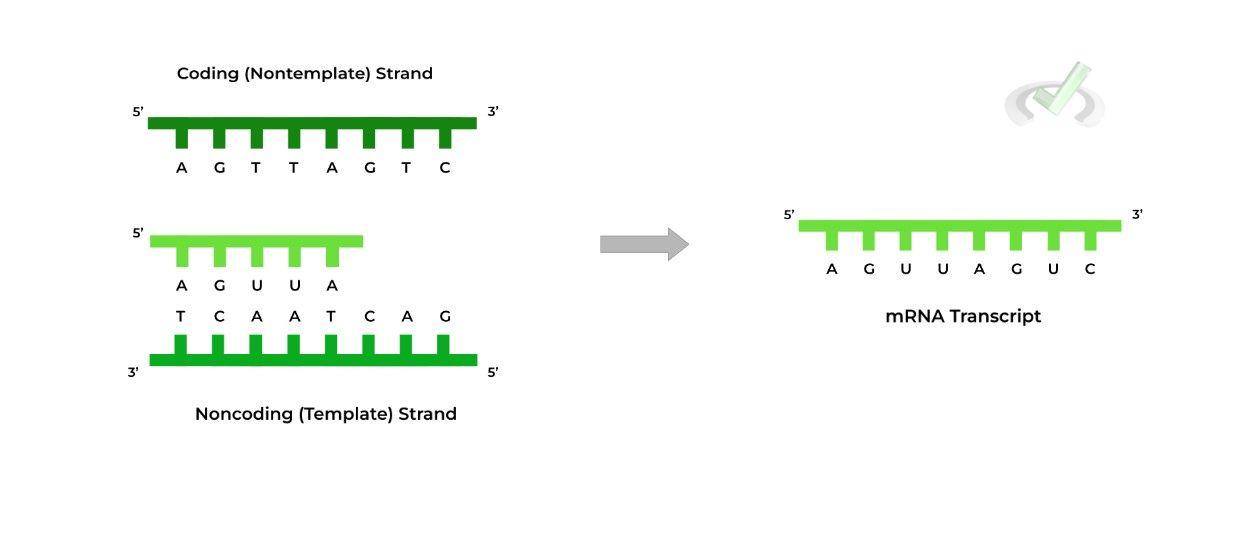
Template And Coding Strand - It contains complementary nucleotide sequences to the transcribed mrna. Most codons specify an amino acid. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same sequence as the rna transcript, except that it. Web the coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (rna). This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Figure 1.22.only one strand of duplex dna codes for a particular product. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. These two strands work together in a dynamic relationship. A always pairs with t, and g with c. Understand the difference between template and coding strands. Web the coding strand provides a reference for the formation of mrna with a similar sequence, while the template strand guides the rna polymerase to synthesize a complementary rna strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Smaller and more mobile than the dna sequence that it is built from, but containing the same information. Most codons specify. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Web jan 6, 2014 at 20:07. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. This way, both strands work together, ensuring the right information. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same sequence as the rna transcript, except that it. The nucleotide at the 5′ end of the chain retains its triphosphate group. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis. What does an mrna transcript look like? The dna strand that codes for the relevant gene is known as the coding strand. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Most codons specify an amino acid. The other strand of the dna is the template for the synthesis of the rna. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web the template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. Web the coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical. The nontemplate strand is referred to. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: Web an mrna transcript is a single strand of rna that encapsulate the information contained in a gene. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Most codons specify an amino acid. The nontemplate strand is. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript.. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The nontemplate strand is referred to. Unlike dna replication, a primer is not needed in rna synthesis. Smaller and more mobile than the dna sequence that it is built from, but containing the same information. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Figure 1.22.only one strand of duplex dna codes for a particular product. What does an mrna transcript look like? Here are some features of codons: This is complementary to the template strand, which may be translated to create an rna fragment with the same nucleotide sequence as the coding strand. Web the coding strand and template strand are two complementary. Cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Jan 6, 2014 at 22:14. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same sequence as the rna transcript, except that it. A always pairs with t, and g with c. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). Web it is also called (+) strand, or nontemplate strand. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. Unlike dna replication, a primer is not needed in rna synthesis. Web jan 6, 2014 at 20:07. Web the template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. This is complementary to the template strand, which may be translated to create an rna fragment with the same nucleotide sequence as the coding strand. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web an mrna transcript is a single strand of rna that encapsulate the information contained in a gene. This way, both strands work together, ensuring the right information is transferred from dna to rna. Web the strand of dna that reads the same as the sequence of mrna is the nontemplate strand.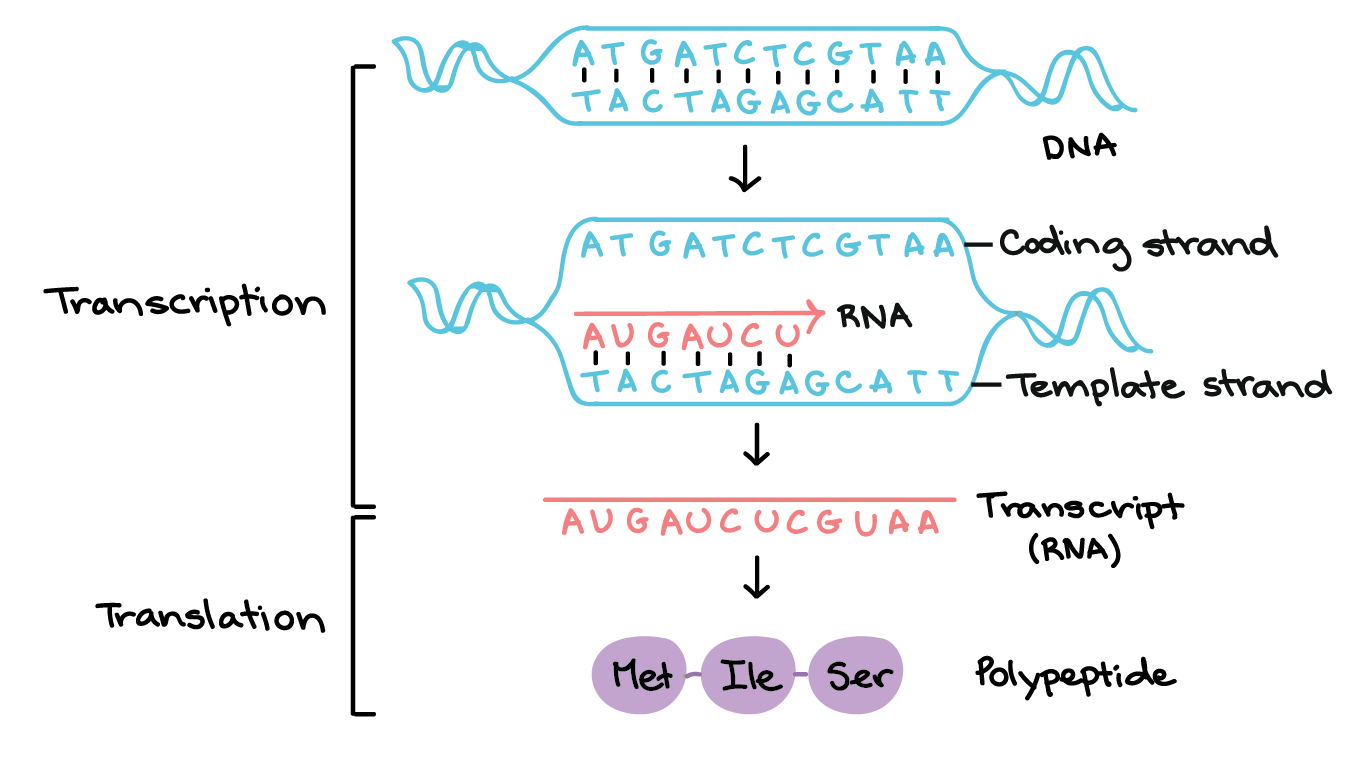
Transcription and Translation
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
DNA Transcription (RNA Synthesis) Article, Diagrams and Video
RNA Transcription Fundamentals and Key Terms on the MCAT MCAT Mastery
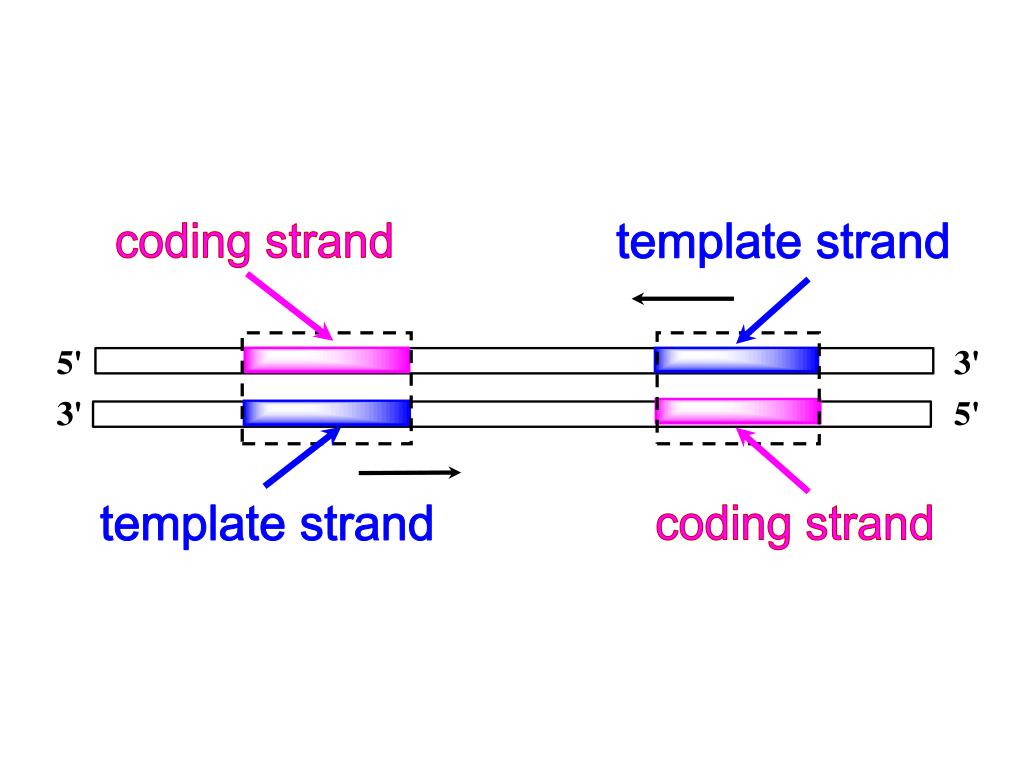
PPT Chapter 11 Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Gene Expression Transcription Agriculture, and Biotechnology

Template Strand Mrna
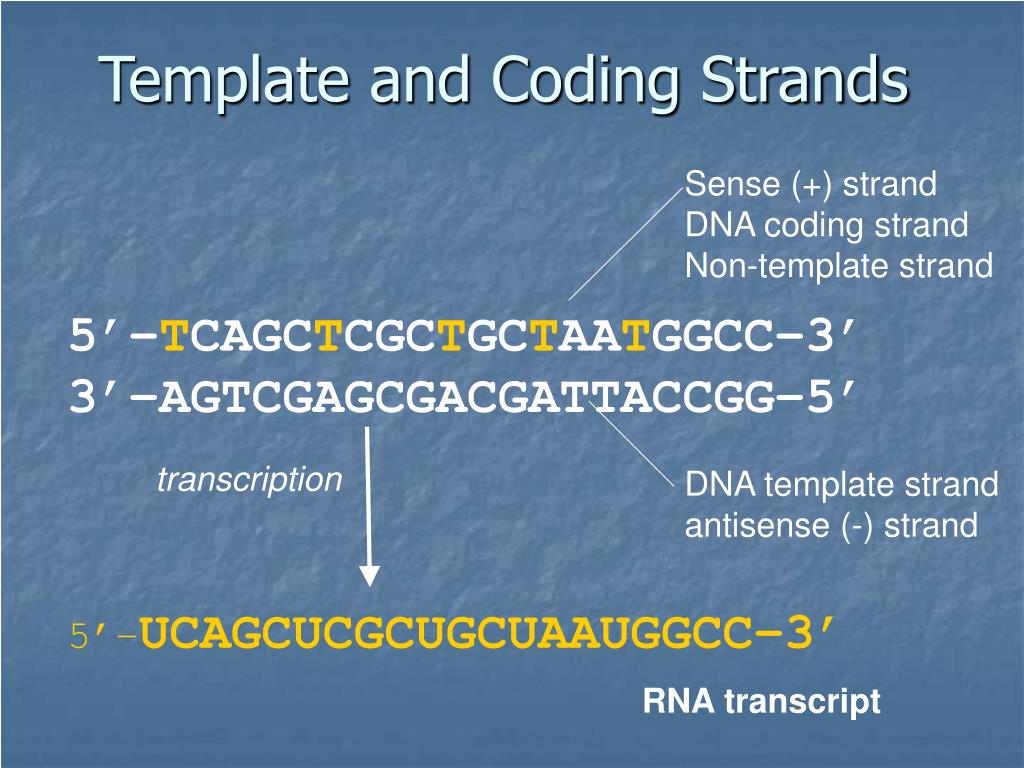
PPT Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1215212
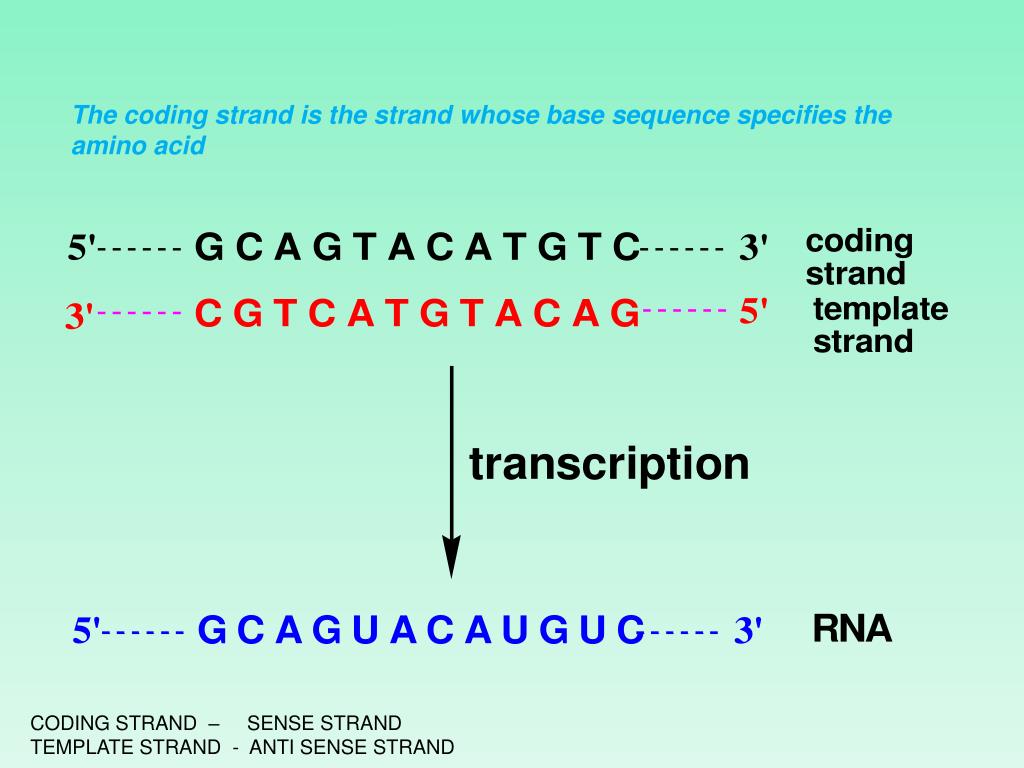
PPT Transcription PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3154392
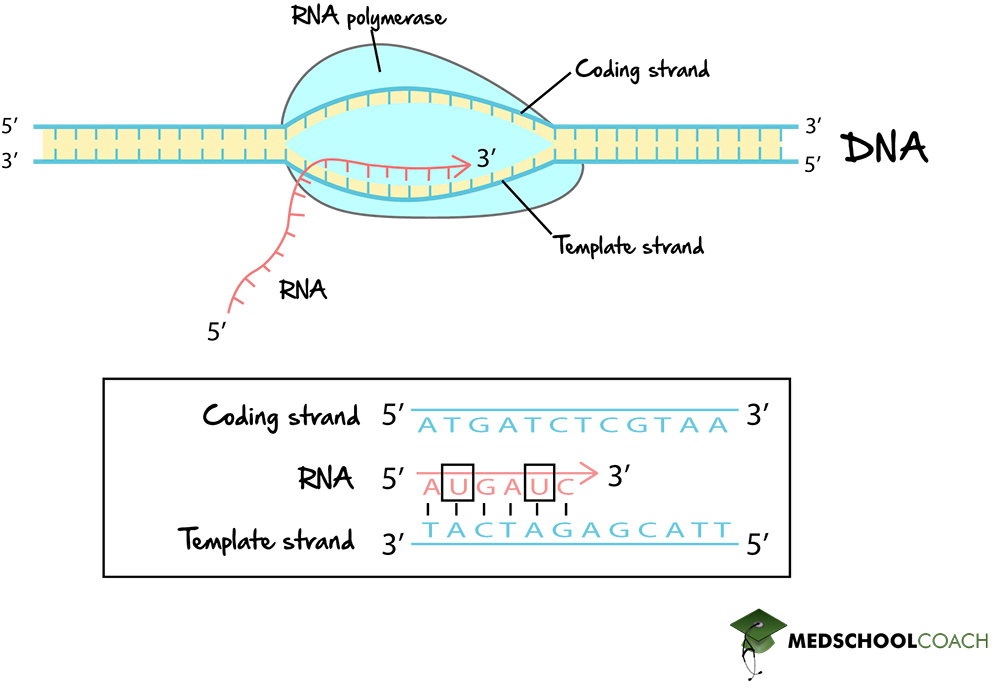
Mechanism of Transcription MCAT Biology MedSchoolCoach
Here Are Some Features Of Codons:
Web The Coding Strand And Template Strand Are Two Complementary Strands Of Dna That Play Different Roles In The Process Of Transcription.
The Template Strand, On The Other Hand, Is Like The Builder’s Scaffold, Providing A Template For The Synthesis Of A New Dna Strand.
Figure 1.22.Only One Strand Of Duplex Dna Codes For A Particular Product.
Related Post: