Extracellular Matrix Drawing
Extracellular Matrix Drawing - The cellular receptors for a number of these ecm components are integrins, although the exact integrin αβ pair may differ. Studies of the extracellular matrix (the material that surrounds cells and tissues) span much of modern biological research. In order to use the ecm as a scaffold in medicine, its cellular fractions need to be removed while retaining its structural and compositional properties. The native ecm promises to provide an excellent scaffold for regenerative medicine. Web in biology, the extracellular matrix (ecm), also called intercellular matrix (icm), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Here, we’ll look in more detail at these external structures and the roles they play in different cell types. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) is a ubiquitous member of the body and is key to the maintenance of tissue and organ integrity. Cell communication within tissue and tissue formation are main functions of the extracellular matrix of animal cells. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) supports cells and regulates various cellular functions in our body. Initially thought to be a bystander in many cellular processes, the extracellular matrix has been shown to have diverse components that regulate and activate many cellular processes and ultimately influence cell phenotype. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) of hyaline cartilage is homogeneous and glassy, rich in in type ii collagen, proteoglycans such as aggrecan, and structural glycoproteins such as chondronectin. Accumulated knowledge clearly demonstrated over the last decade that ecm plays key regulatory roles since it orchestrates cell signaling, functions, properties and morphology. The extracellular matrix of animal cells is made up. Cell communication within tissue and tissue formation are main functions of the extracellular matrix of animal cells. The cellular receptors for a number of these ecm components are integrins, although the exact integrin αβ pair may differ. The ecm in mammals is composed of around 300 proteins, known as the core. Web the extracellular matrix is mostly made up of. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) of hyaline cartilage is homogeneous and glassy, rich in in type ii collagen, proteoglycans such as aggrecan, and structural glycoproteins such as chondronectin. Web the extracellular matrix is a mesh structure made of water and diverse proteins and carbohydrates, which surround a cell. Water, fibrous proteins, and proteoglycans. The native ecm promises to provide an. The main fibrous proteins that build the extracellular matrix are collagens, elastins, and laminins. Web extracellular matrix is a general term for the extremely large proteins and polysaccharides that are secreted by some cells in a multicellular organism, and which acts as connective material to hold cells in a defined space. Web basically only animal cells have ecm or extracellular. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) is a dynamic structure that is constantly remodelled to control tissue homeostasis. Web plants and fungi have a tough cell wall for protection and support, while animal cells can secrete materials into their surroundings to form a meshwork of macromolecules called the extracellular matrix. Virginia tech carilion school of medicine via virginia tech libraries' open. Adhesive proteins, structural proteins, and proteoglycans. Ecm in muscle fiber niche consists of three layers: Can circulate in plasma to assist with clotting. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) refers to the mixture of proteins and carbohydrates that surrounds cells and provides structural and biochemical support. Web basically only animal cells have ecm or extracellular matrix, because plants have their tough. Extracellular matrix (ecm) is a kind of connective tissue in the cell microenvironment, which is of great significance to tissue development. Web extracellular matrix is a general term for the extremely large proteins and polysaccharides that are secreted by some cells in a multicellular organism, and which acts as connective material to hold cells in a defined space. Web the. Studies of the extracellular matrix (the material that surrounds cells and tissues) span much of modern biological research. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) supports cells and regulates various cellular functions in our body. The extracellular matrix of animal cells is made up of proteins and carbohydrates. Web extracellular matrix is a. Water, fibrous proteins, and proteoglycans. Initially thought to be a bystander in many cellular processes, the extracellular matrix has been shown to have diverse components that regulate and activate many cellular processes and ultimately influence cell phenotype. The name extracellular matrix mainly refers to the components found outside of animal cells. Typical components include collagen, proteoglycans (with hydration shell depicted. (i) polysaccharide glycosaminoglycan’s (commonly known as mucopolysaccharides) or gags which are usually linked covalently to proteins in the form of proteoglycans; It also forms a few specialized structures such as cartilage, tendons, and the basement membrane (also called the basal lamina). Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: The main fibrous proteins that build the extracellular matrix are collagens, elastins, and laminins.. The cellular receptors for a number of these ecm components are integrins, although the exact integrin αβ pair may differ. The name extracellular matrix mainly refers to the components found outside of animal cells. The extracellular matrix of animal cells is made up of proteins and carbohydrates. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web extracellular matrix (ecm). Virginia tech carilion school of medicine via virginia tech libraries' open education initiative. Ecm components can be put into three categories: Web extracellular matrix is a general term for the extremely large proteins and polysaccharides that are secreted by some cells in a multicellular organism, and which acts as connective material to hold cells in a defined space. (i) polysaccharide glycosaminoglycan’s (commonly known as mucopolysaccharides) or gags which are usually linked covalently to proteins in the form of proteoglycans; Web the extracellular matrix is made of three main types of extracellular macromolecules: Accumulated knowledge clearly demonstrated over the last decade that ecm plays key regulatory roles since it orchestrates cell signaling, functions, properties and morphology. It also forms a few specialized structures such as cartilage, tendons, and the basement membrane (also called the basal lamina). Web basically only animal cells have ecm or extracellular matrix, because plants have their tough cell walls that support and protect them. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Typical components include collagen, proteoglycans (with hydration shell depicted around sugars), bronectin, and laminin. Ecm in muscle fiber niche consists of three layers: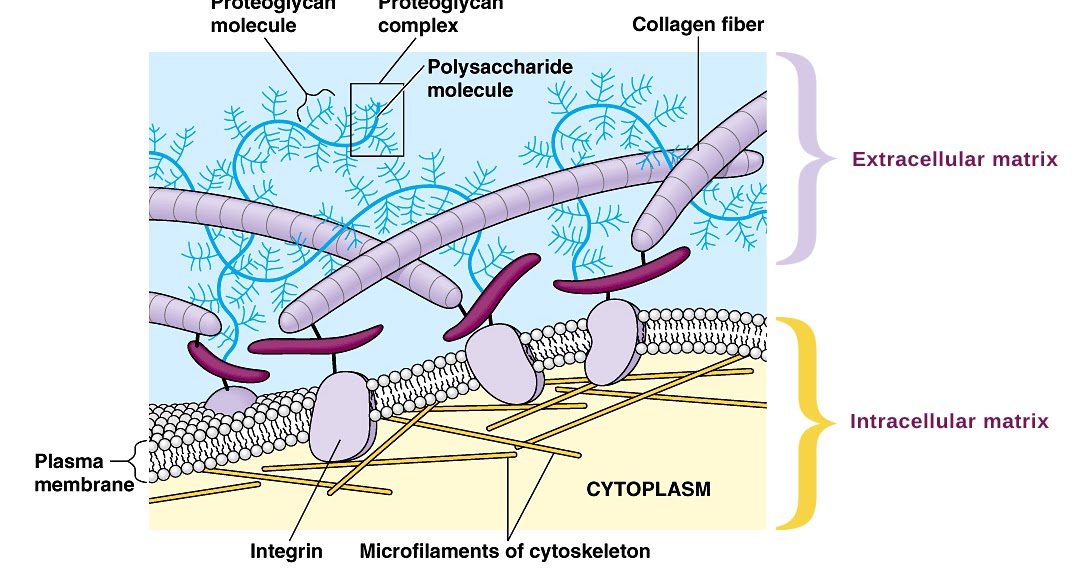
The ECM and Cancer Purpose and Structure of the Extracellular Matrix
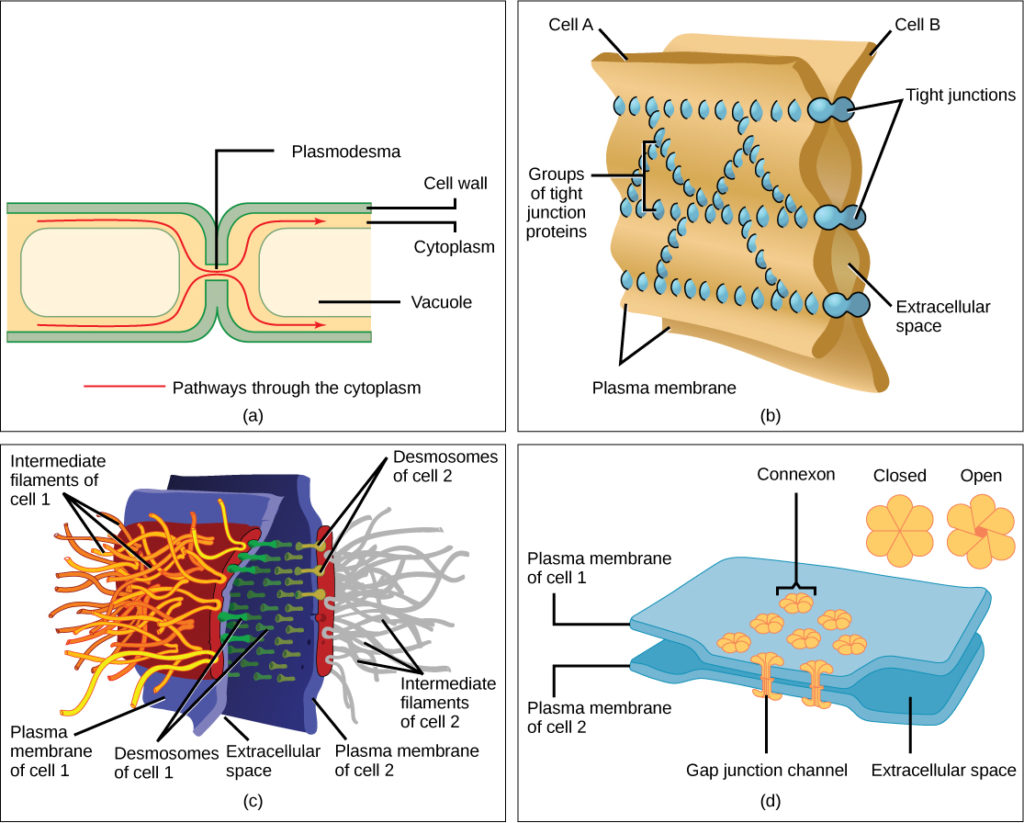
Extracellular matrix and intercellular junctions Mt Hood Community

Schematic overview of extracellular matrix and its major components

Extracellular matrix labeled infographic vector illustration scheme

Extracellular Matrix Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1

A schematic drawing of the extracellular matrix molecular organization

Schematic representation of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen

Fibronectin A Cell Adhesion and Blood Clotting Protein Owlcation
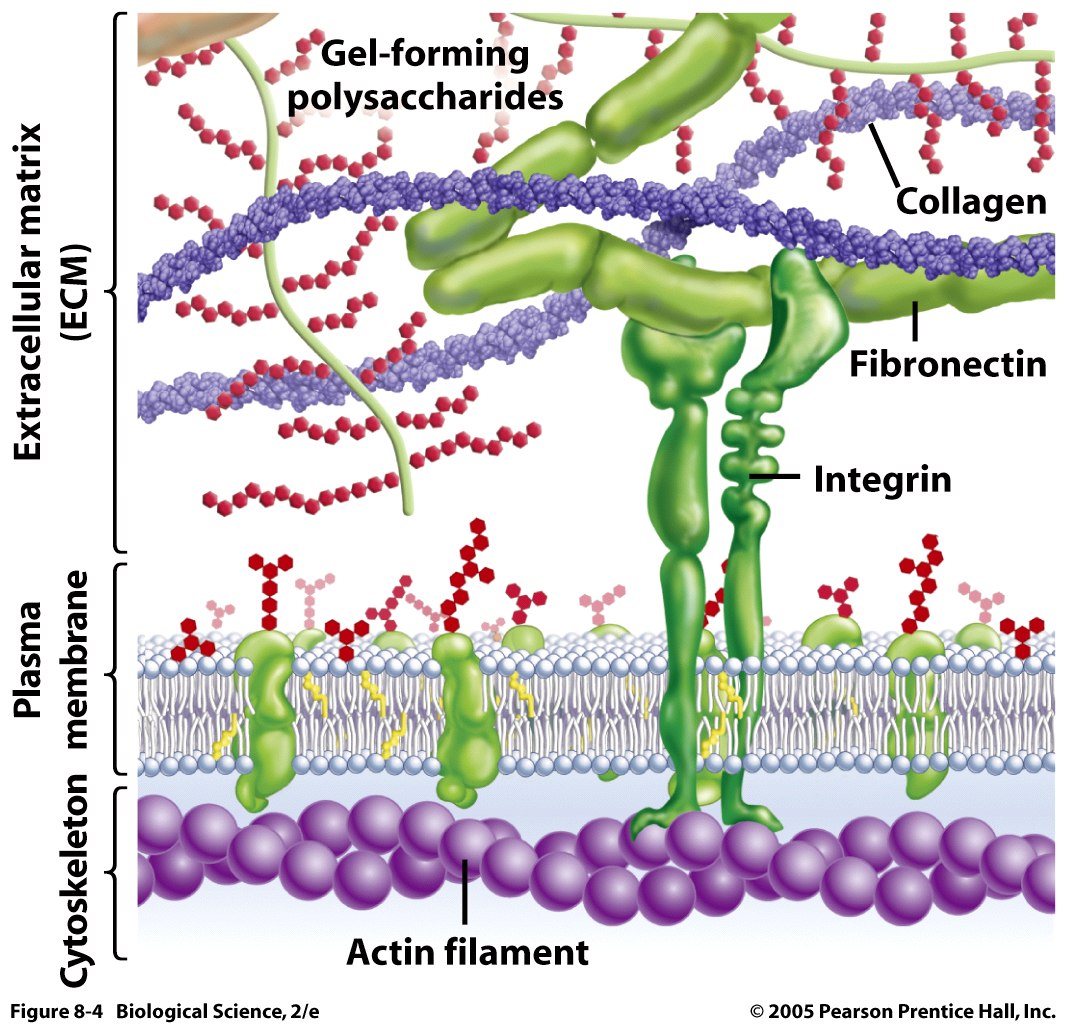
Extra Cellular Matrix Is Critical to Neuroplasticity
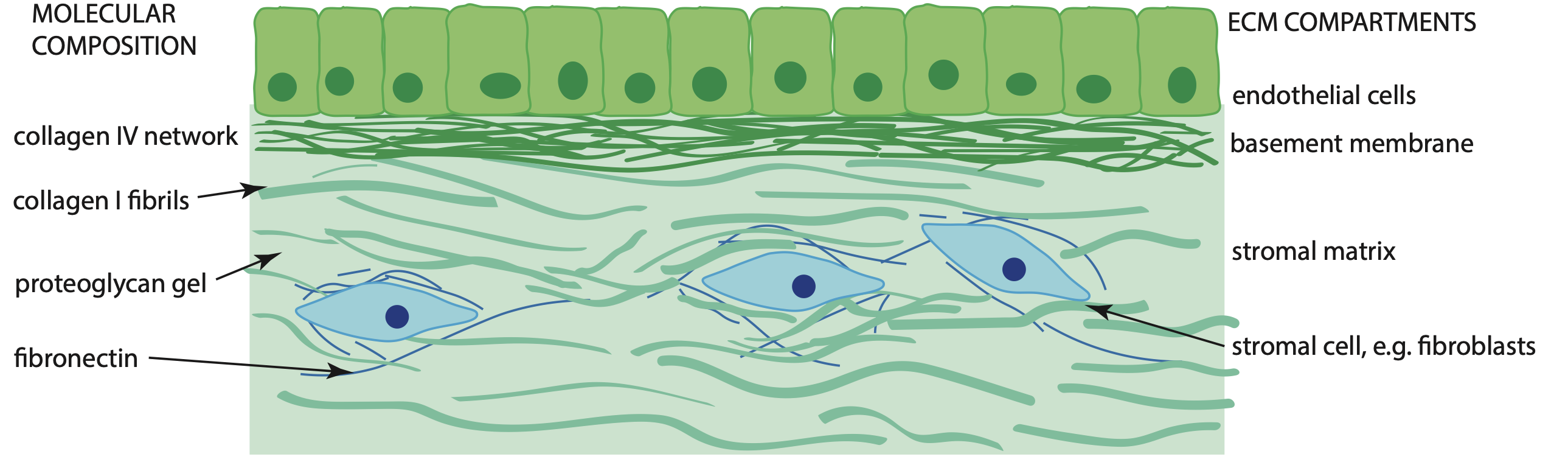
The molecular structure of the extracellular matrix Duer Research Group
Adhesive Proteins, Structural Proteins, And Proteoglycans.
Initially Thought To Be A Bystander In Many Cellular Processes, The Extracellular Matrix Has Been Shown To Have Diverse Components That Regulate And Activate Many Cellular Processes And Ultimately Influence Cell Phenotype.
(Ii) Fibrous Proteins Of Two Functional Types:
The Epimysium, The Perimysium, And The Endomysium (Basal Lamina).
Related Post: