During Which Process Is Mrna Synthesized From A Dna Template
During Which Process Is Mrna Synthesized From A Dna Template - The lagging strand is synthesized in pieces. 1 ), which states that genes specify. Here is an overview of the central dogma. Web mrna is created during transcription. Mrna is made from a dna template during the. Web transcription has three stages: Web go to lesson page. To illustrate utility, we constructed five unique. These mrna transcripts escape the. Web how does transcription proceed? They are spliced and have a 5' cap and. During the transcription process, a single strand of dna is decoded by rna polymerase, and mrna is synthesized. Web figure 11.11 during elongation, the bacterial rna polymerase tracks along the dna template, synthesizes mrna in the 5’ to 3’ direction, and unwinds and rewinds the dna. Web we present a method. Mrna, which stands for messenger rna, is synthesized during the process of transcription, not translation. Dna safely and stably stores genetic. In eukaryotes, rna molecules must be processed after transcription: The process of transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase (rna pol) attaches to the template dna strand and begins to catalyze. These mrna transcripts escape the. The process of transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase (rna pol) attaches to the template dna strand and begins to catalyze. To illustrate utility, we constructed five unique. Web how does transcription proceed? Web the process occurs in two steps: Mrna, which stands for messenger rna, is synthesized during the process of transcription, not translation. Web the flow of genetic information in cells from dna to mrna to protein is described by the central dogma (figure 9.3.1 9.3. Here is an overview of the central dogma. In contrast, the single mrna molecule is synthesized as a continuous. Translation = rna → protein. Web mrna is created during transcription. In transcription, the dna's code is copied to. 1 ), which states that genes specify. Web the process occurs in two steps: The process of transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase (rna pol) attaches to the template dna strand and begins to catalyze. The primary transcript that is synthesized by the rna polymerase. Web during this process, an adenine (a) in the dna binds to an uracil (u) in the rna. The primary transcript that is synthesized by the rna polymerase. Web transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of dna is copied into a new molecule of messenger rna (mrna). Web the process occurs in two steps: Web. Web the process occurs in two steps: Web go to lesson page. Web draw a line diagram showing a segment of dna from a gene and its rna transcript, indicating which dna strand is the template, the direction of transcription and the. Termination is the ending of transcription, and occurs when rna polymerase crosses a. Translation = rna → protein. Web transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of dna is copied into a new molecule of messenger rna (mrna). Bacterial mrnas do not undergo any significant forms of processing: Web how does transcription proceed? Web the flow of genetic information in cells from dna to mrna to protein is described by the central dogma (figure. 1 ), which states that genes specify. Web during this process, an adenine (a) in the dna binds to an uracil (u) in the rna. In transcription, the dna's code is copied to. Web rna polymerase synthesizes rna, using the antisense strand of the dna as template by adding complementary rna nucleotides to the 3’ end of the growing. Bacterial. The process of transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase (rna pol) attaches to the template dna strand and begins to catalyze. Web the process occurs in two steps: Bacterial mrnas do not undergo any significant forms of processing: Web figure 11.11 during elongation, the bacterial rna polymerase tracks along the dna template, synthesizes mrna in the 5’ to. Web draw a line diagram showing a segment of dna from a gene and its rna transcript, indicating which dna strand is the template, the direction of transcription and the. Termination is the ending of transcription, and occurs when rna polymerase crosses a. Web how does transcription proceed? During the transcription process, a single strand of dna is decoded by rna polymerase, and mrna is synthesized. The lagging strand is synthesized in pieces. In contrast, the single mrna molecule is synthesized as a continuous. Transcription = dna → rna. Mrna is made from a dna template during the. Mrna, which stands for messenger rna, is synthesized during the process of transcription, not translation. Web mrna is created during transcription. Web the process occurs in two steps: Transcription begins when an enzyme called rna polymerase attaches to the dna template strand and begins assembling a new chain. Web transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of dna is copied into a new molecule of messenger rna (mrna). Web during elongation, an enzyme called rna polymerase proceeds along the dna template adding nucleotides by base pairing with the dna template in a manner similar to dna. Web transcription has three stages: Web go to lesson page.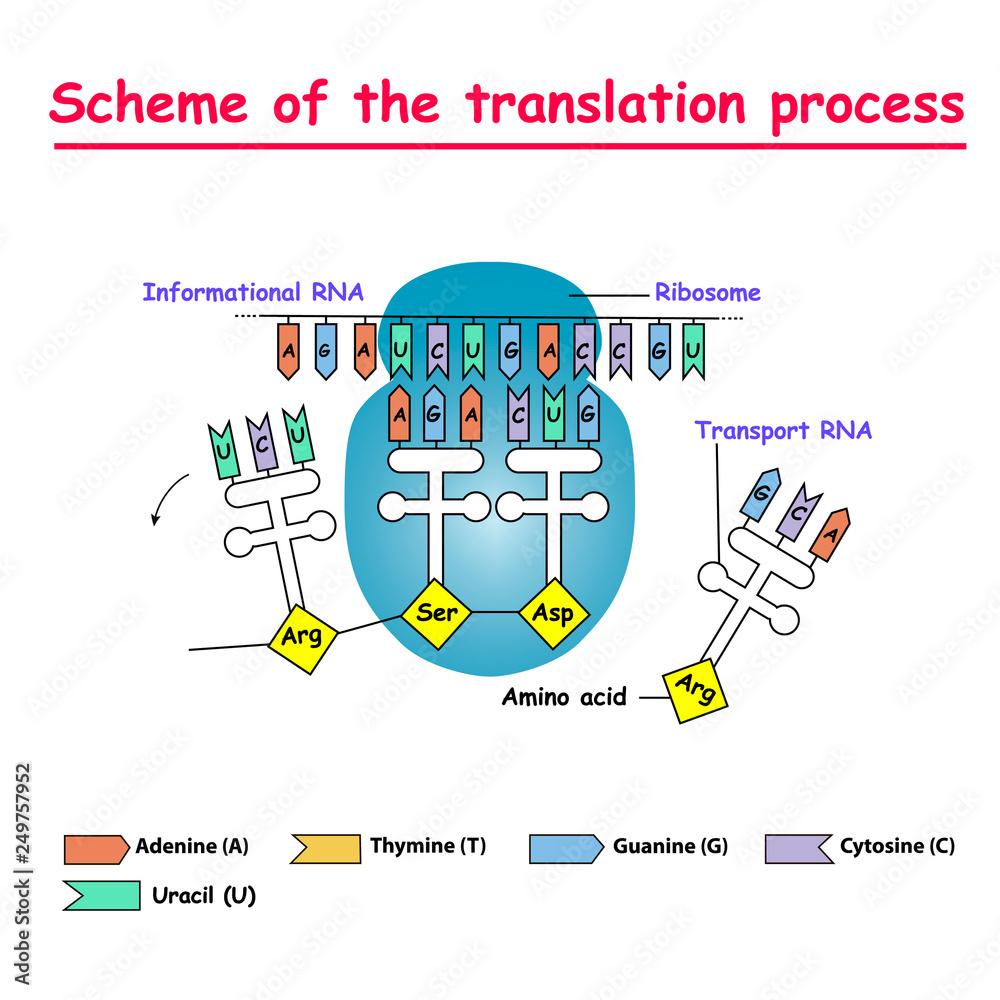
Fototapeta Scheme of the translation process. syntesis of mRNA from DNA
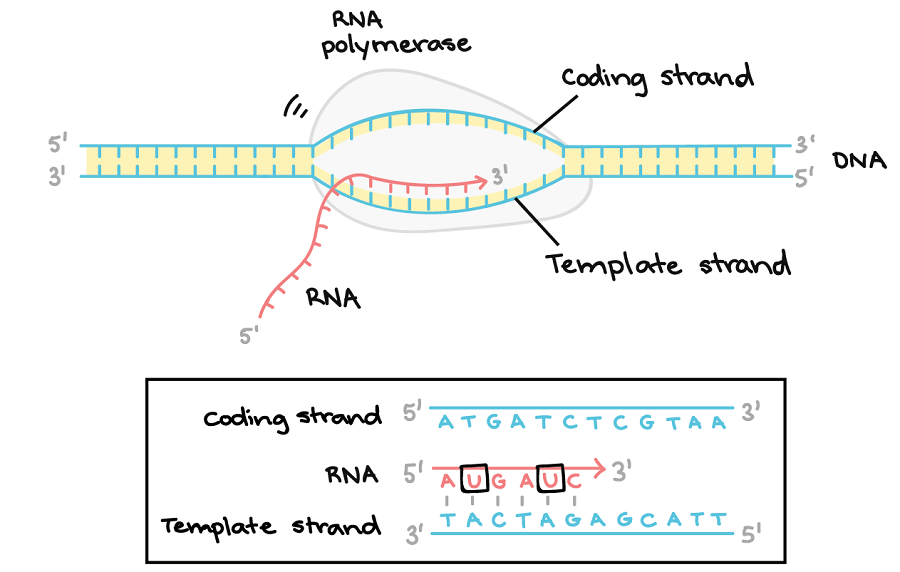
DNA Transcription (RNA Synthesis) Article, Diagrams and Video

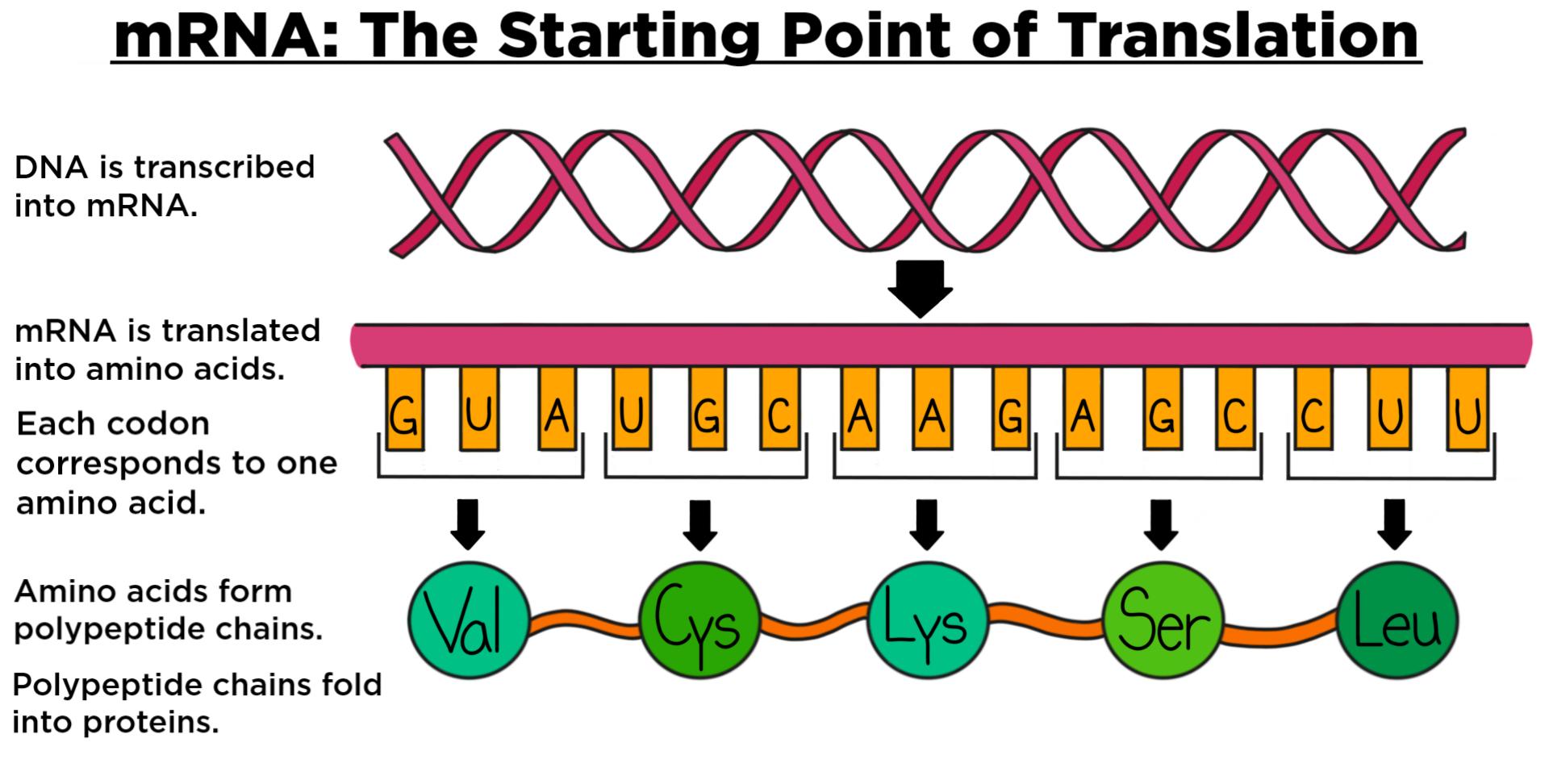
Translation DNA to mRNA to Protein Learn Science at Scitable
What Are The 3 Types Of Rna And What Are Their Functions slideshare
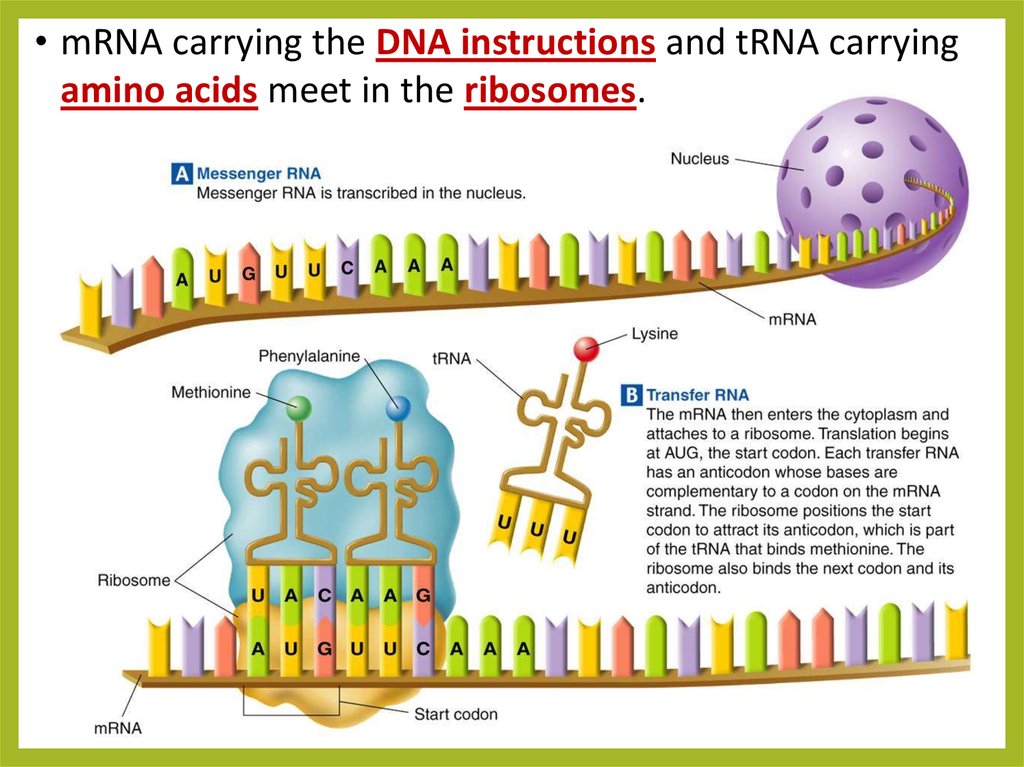
Protein synthesis презентация онлайн

Images of ADNA JapaneseClass.jp
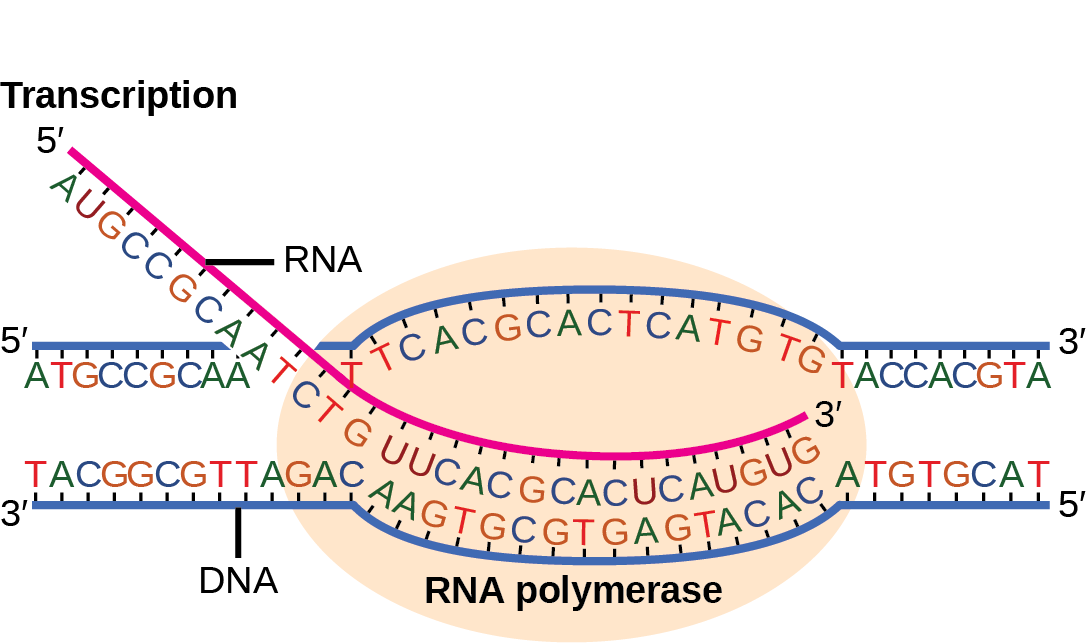
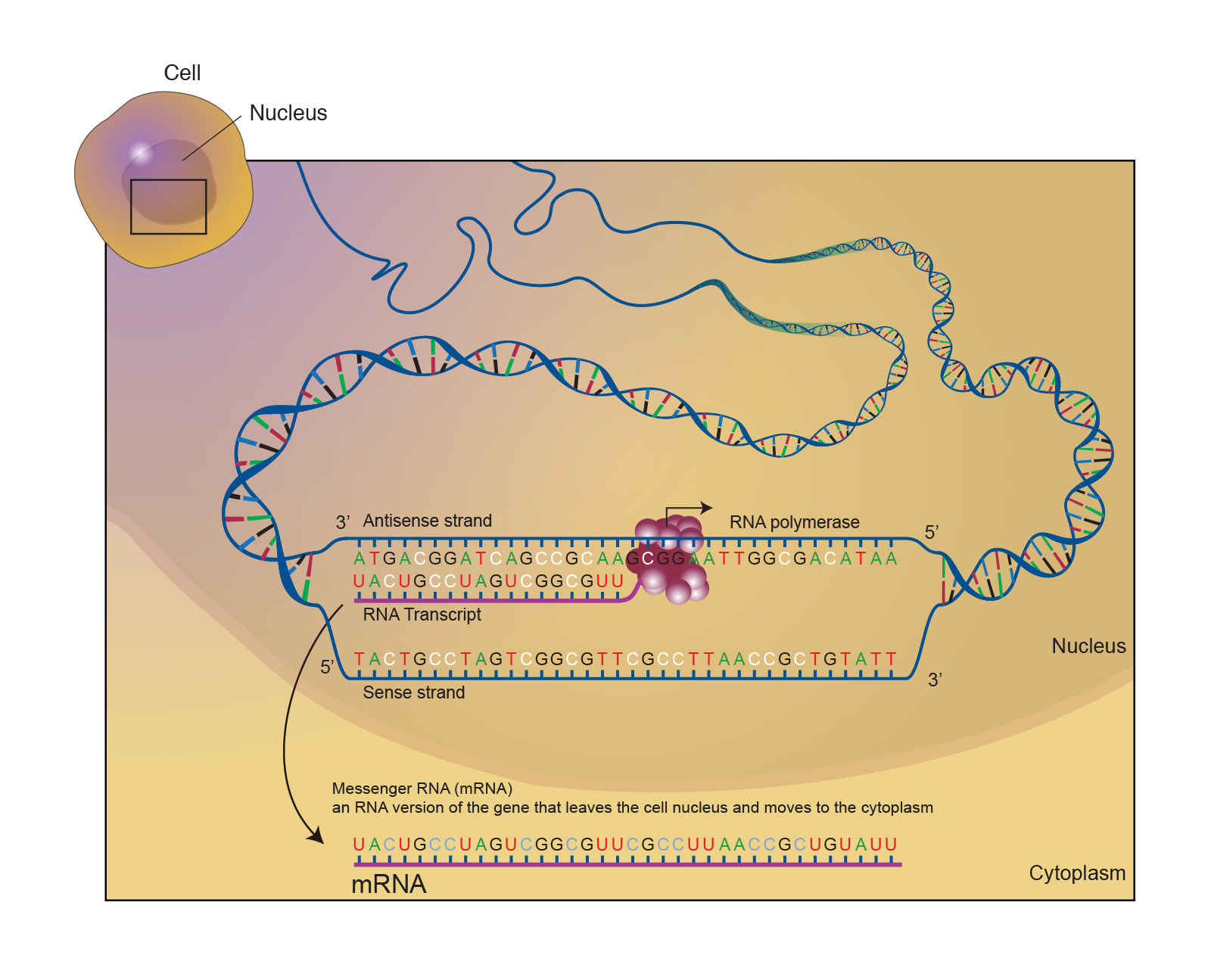
23.2 Prokaryotic Transcription Biology 110 PSU Dubois
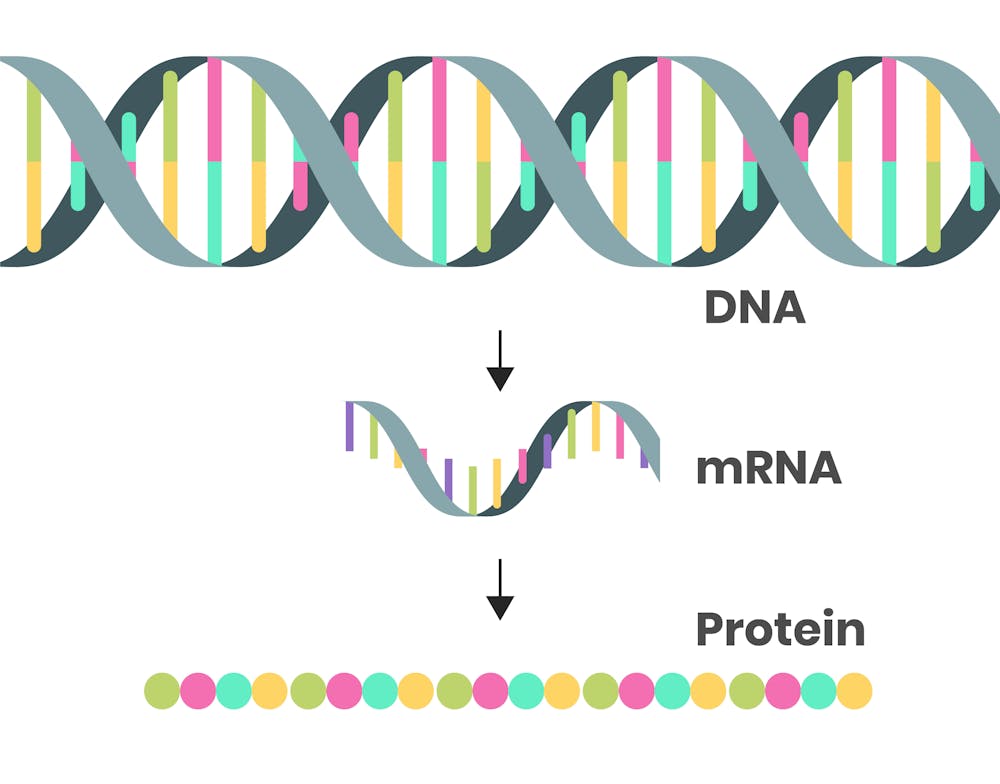
What is mRNA? The messenger molecule that's been in every living cell
Analyzing tumor RNA may help match patients with most effective cancer
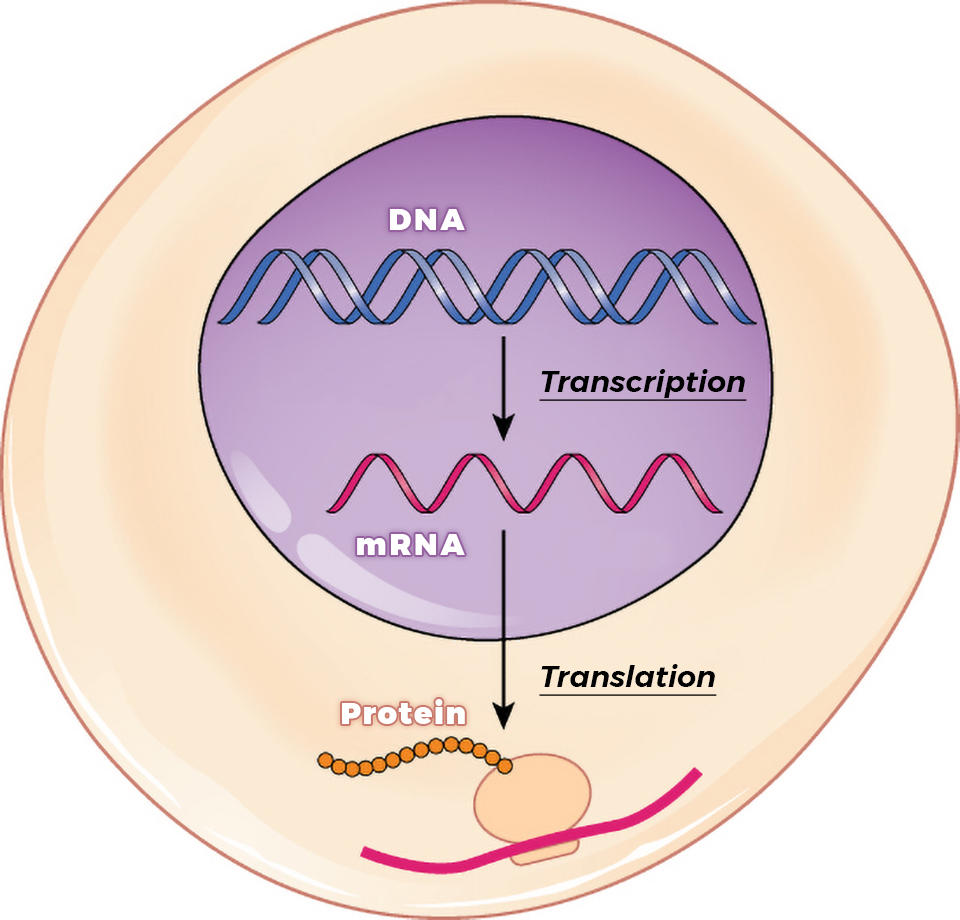
Messenger RNA (mRNA) — Overview & Role in Translation Expii
1 ), Which States That Genes Specify.
Translation = Rna → Protein.
Web The Flow Of Genetic Information In Cells From Dna To Mrna To Protein Is Described By The Central Dogma (Figure 9.3.1 9.3.
Web We Present A Method To Synthesize Mrnas From Synthetic Dna Templates That Produce Biologically Active Proteins.
Related Post: