Drawing Of Hydrological Cycle
Drawing Of Hydrological Cycle - Web this article provides a diagram of hydrological cycle. Under anthropogenic global warming, previous studies showed that the intensification of the hydrologic cycle is a robust feature. The hydrologic cycle has wide impacts on the ocean salinity and circulation, carbon and nitrogen cycles, and the ecosystem. Web diagram of the water cycle. Web diagram of the water cycle. Water is constantly on the move. Notably, this new water cycle diagram depicts humans and major categories of human water use as key components of the water cycle, in addition to the key pools and fluxes of the hydrologic. Earth science, meteorology, geography, physical geography, geology. Water is always changing states between liquid, vapor, and ice, with these processes happening in the blink of an eye and over millions of years. A diagram of the water cycle showing evaporation, condensation, precipitation and more. Water is constantly on the move. A diagram of the water cycle showing evaporation, condensation, precipitation and more. The mass of water on earth remains fairly constant over time. Notably, this new water cycle diagram depicts humans and major categories of human water use as key components of the water cycle, in addition to the key pools and fluxes of. Liquid water can be fresh or saline (salty). The process by which water from its liquid state changes to vapour, a gaseous state, is termed as evaporation. The hydrologic cycle, or water cycle, is the cycling of water through the earth system. This is a modern, updated version of the widely used diagram featured on the usgs water science school.. Web earth's water is always in movement, and the natural water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the earth. This is a modern, updated version of the widely used diagram featured on the usgs water science school. Web the water cycle, or hydrologic cycle, is driven. The sun acts as the primary source of energy that powers the water cycle on earth. Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, groundwater, runoff, snowmelt, evapotranspiration. A diagram of the water cycle showing evaporation, condensation, precipitation and more. Web an illustrated diagram of the water cycle. Web the complete water cycle is carried into four stages which are as follows: Web the complete water cycle is carried into four stages which are as follows: Notably, this new water cycle diagram depicts humans and major categories of human water use as key components of the water cycle, in addition to the key pools and fluxes of the hydrologic. The mass of water on earth remains fairly constant over time. Web the. Water moves between the places it is stored. A diagram of the water cycle showing evaporation, condensation, precipitation and more. Water is constantly on the move. Web [1] the water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle ), is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the earth. Notably, this. Studies have revealed that evaporation—the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas—from oceans, seas, and other bodies of water (lakes, rivers, streams) provides nearly 90% of the moisture in our atmosphere. A diagram of the water cycle showing evaporation, condensation, precipitation and more. Web an illustrated diagram of the water cycle. Water is constantly on the. Web the complete water cycle is carried into four stages which are as follows: Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, groundwater, runoff, snowmelt, evapotranspiration. The process by which water from its liquid state changes to vapour, a gaseous state, is termed as evaporation. Web diagram of the water cycle. Web [1] the water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle ), is a. It can be a liquid, a solid, or a gas. Earth science, meteorology, geography, physical geography, geology. Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, groundwater, runoff, snowmelt, evapotranspiration. Web the water cycle, or hydrologic cycle, is driven by the sun’s energy. It is evaporated by solar energy from the oceans, lakes, streams, the surface of the land, and from plants (transpiration) (figure 11.1.1). When water droplets in clouds get heavy, they fall to earth as precipitation—rain, snow, hail, and sleet. A diagram of the water cycle showing evaporation, condensation, precipitation and more. Water is constantly on the move. The water cycle describes how water is exchanged (cycled) through earth's land, ocean, and atmosphere. The mass of water on earth remains fairly constant over. Web diagram of the water cycle. (ii) another part flows over the surface in rivers and ultimately reaches sea or ocean. The hydrologic cycle, or water cycle, is the cycling of water through the earth system. Notably, this new water cycle diagram depicts humans and major categories of human water use as key components of the water cycle, in addition to the key pools and fluxes of the hydrologic cycle. The hydrologic cycle has wide impacts on the ocean salinity and circulation, carbon and nitrogen cycles, and the ecosystem. The sun acts as the primary source of energy that powers the water cycle on earth. It can be a liquid, a solid, or a gas. Not only is the hydrologic cycle a cycle of water, it. Web the complete water cycle is carried into four stages which are as follows: Notably, this new water cycle diagram depicts humans and major categories of human water use as key components of the water cycle, in addition to the key pools and fluxes of the hydrologic. Earth's water is always in motion, and the natural water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the earth. Whether this trend persists in hothouse climates, however, is unknown. Earth science, meteorology, geography, physical geography, geology. This is a modern, updated version of the widely used diagram featured on the usgs water science school. The water cycle describes how water is exchanged (cycled) through earth's land, ocean, and atmosphere. Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, groundwater, runoff, snowmelt, evapotranspiration.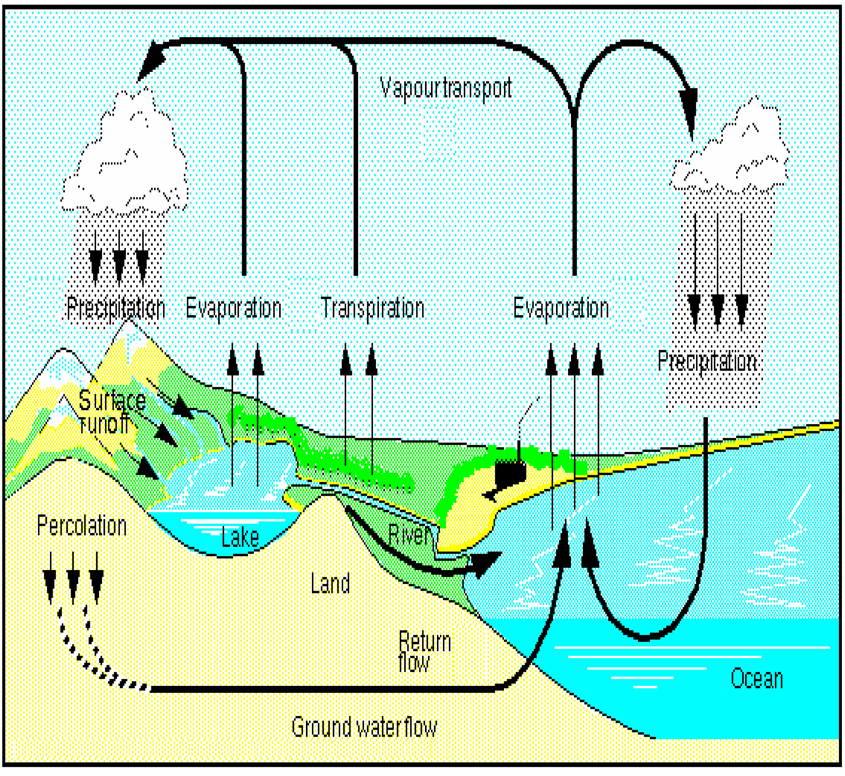
Hydrological Cycle

How to Draw the Water Cycle Really Easy Drawing Tutorial
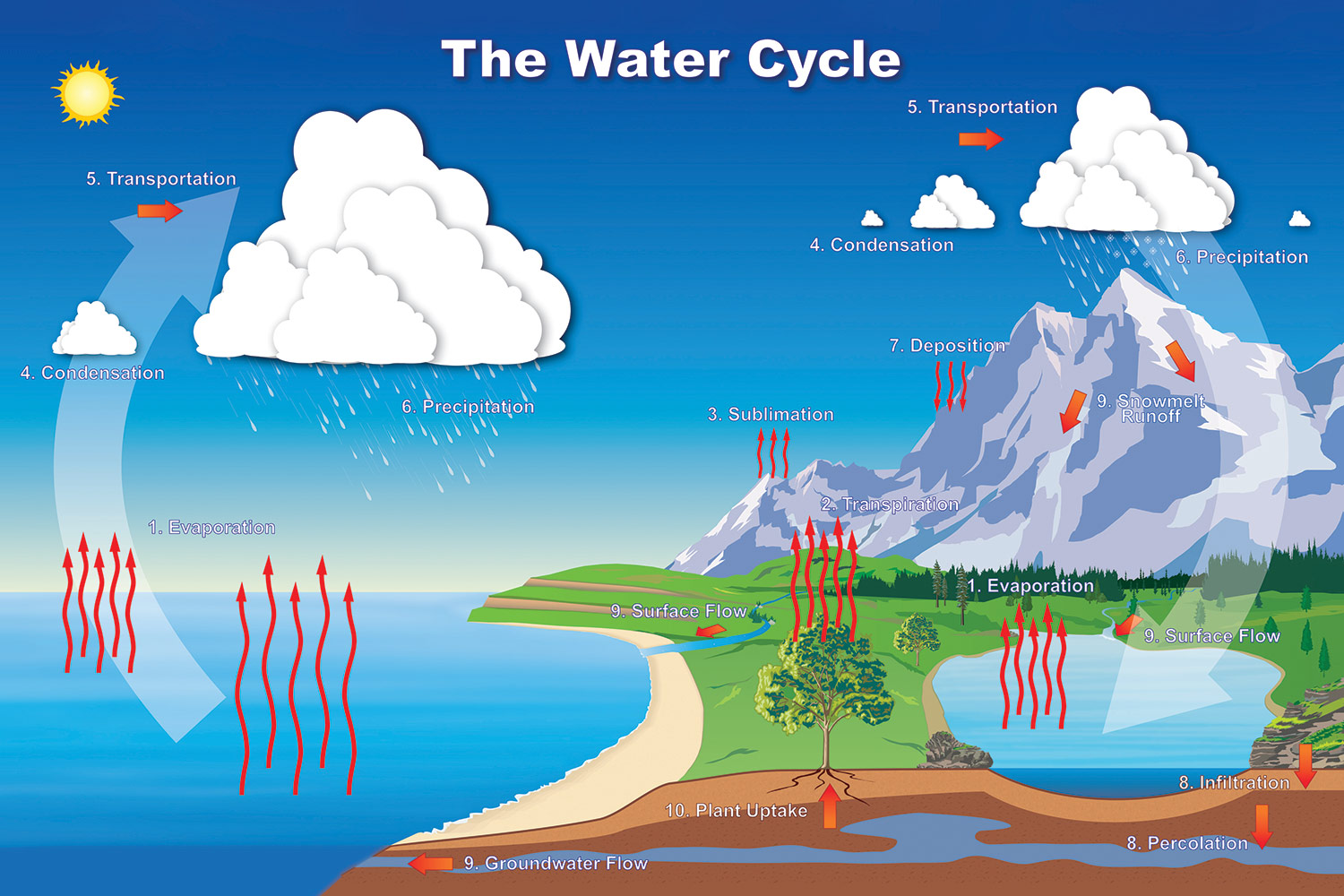
Hydrologic Cycle National Maritime Historical Society

The Hydrological Cycle CIVIL ENGINEERING SOLUTION
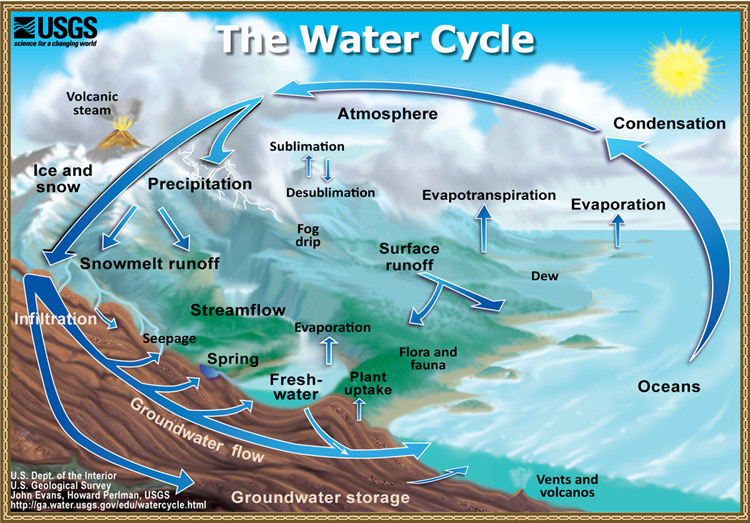
Hydrologic cycle Energy Education

Hydrology and Hydrological Cycle in Water Resource Engineering
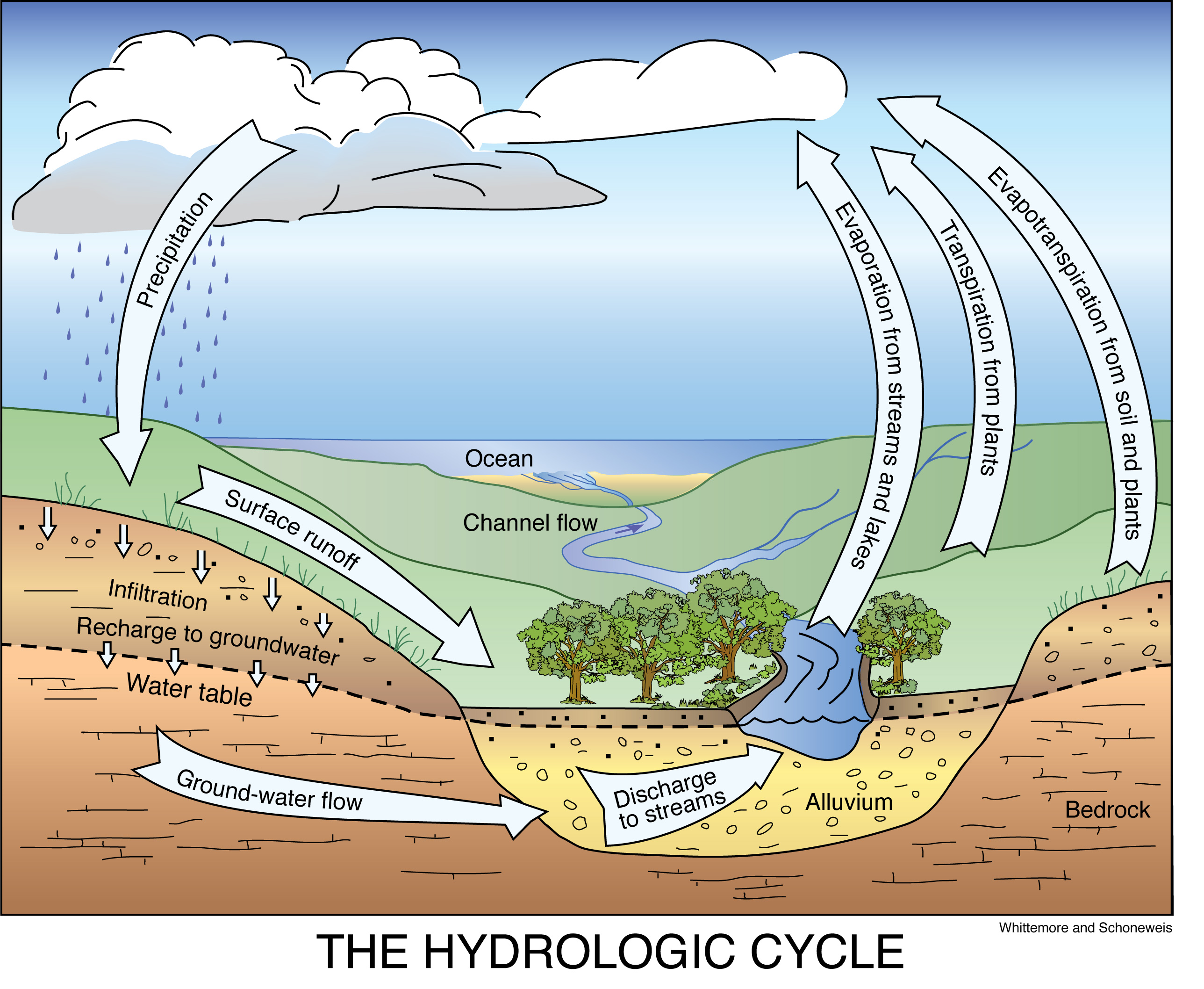
The hydrologic (water) cycle GeoKansas
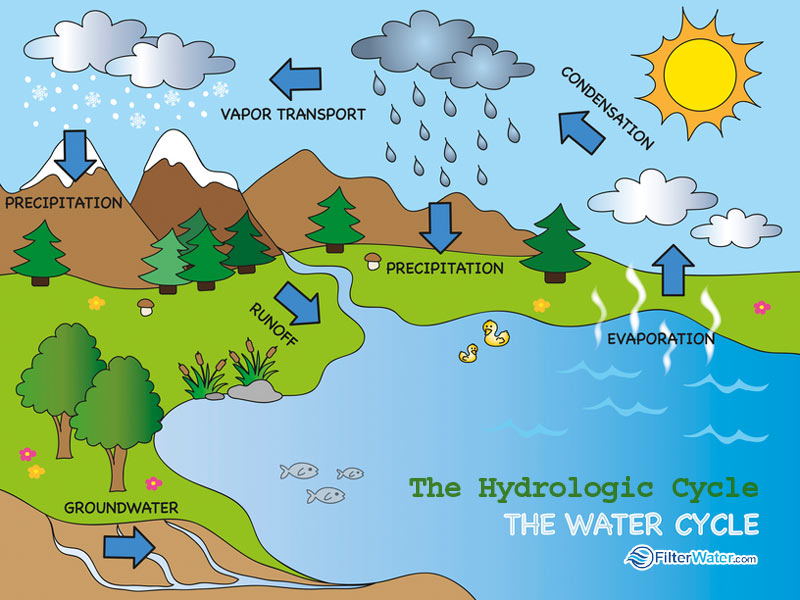
What is Water?
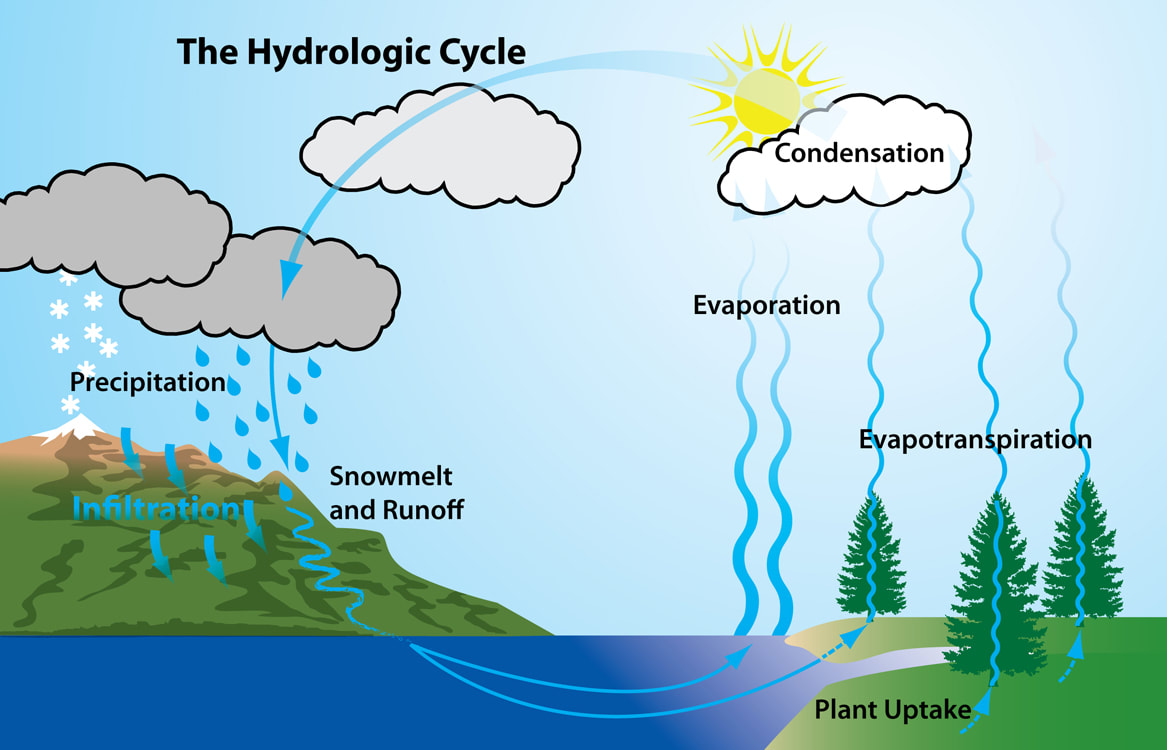
The hydrological Cycle notesychs
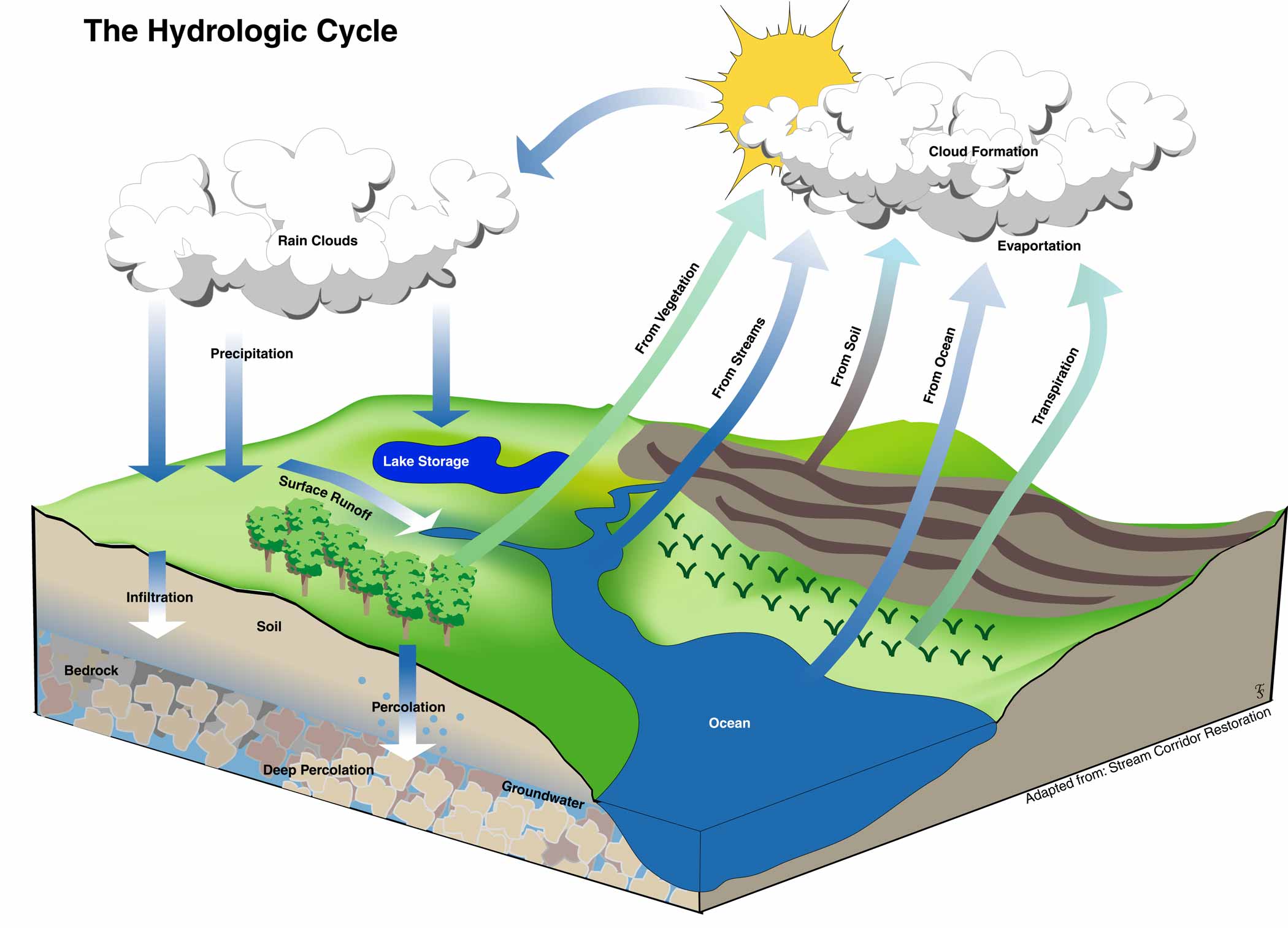
HydrologicCycle FWEE
Our Newest Diagram, Released In 2022, Depicts The Global Water Cycle, As Well As How Human Water Use Affects Where Water Is Stored, How It Moves, And How Clean It Is.
Web Diagram Of The Water Cycle.
The Mass Of Water On Earth Remains Fairly Constant Over Time.
Of The Many Processes Involved In The Hydrologic Cycle, The Most Important Are:
Related Post: