Drawing Of Blood Vessels
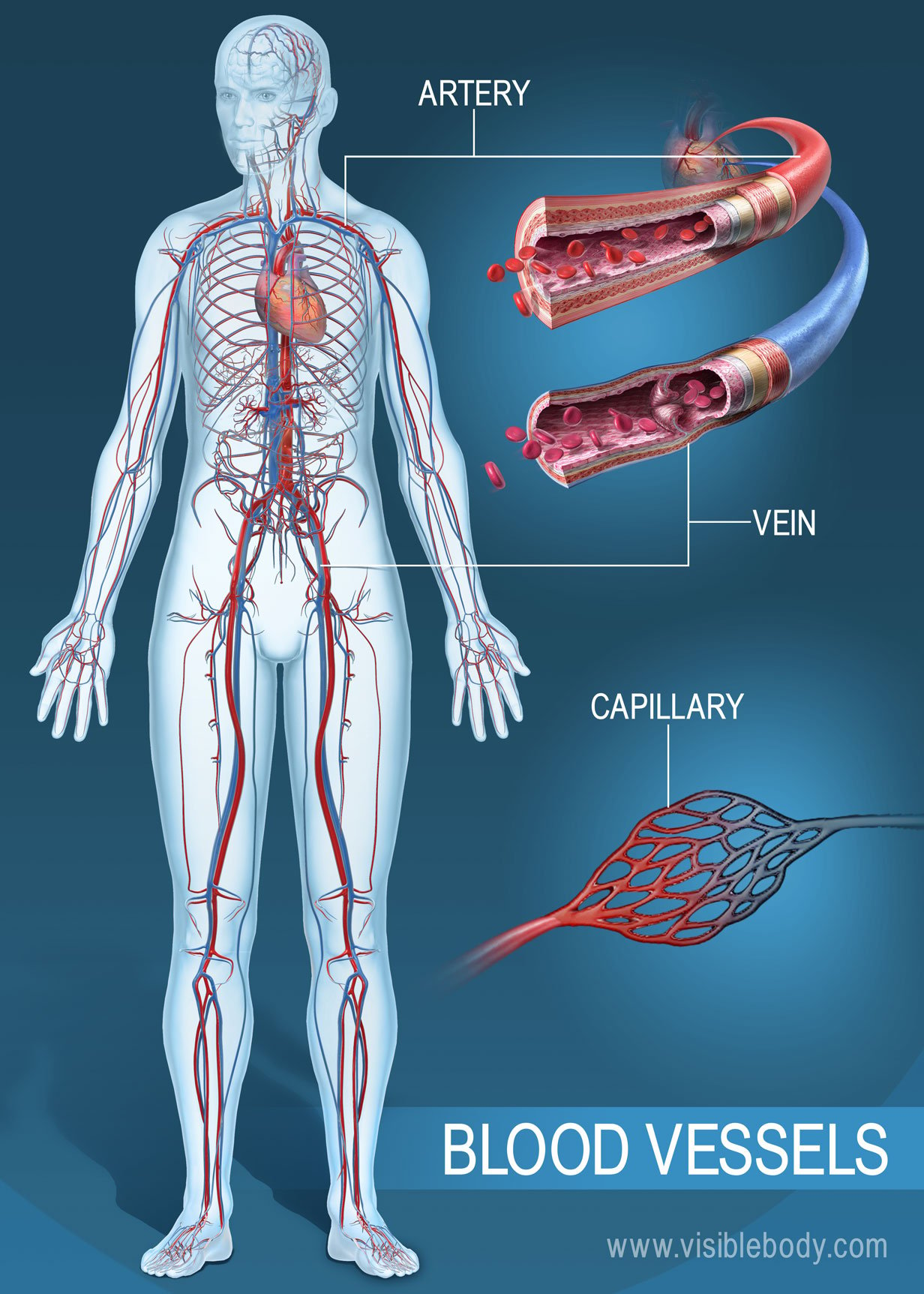
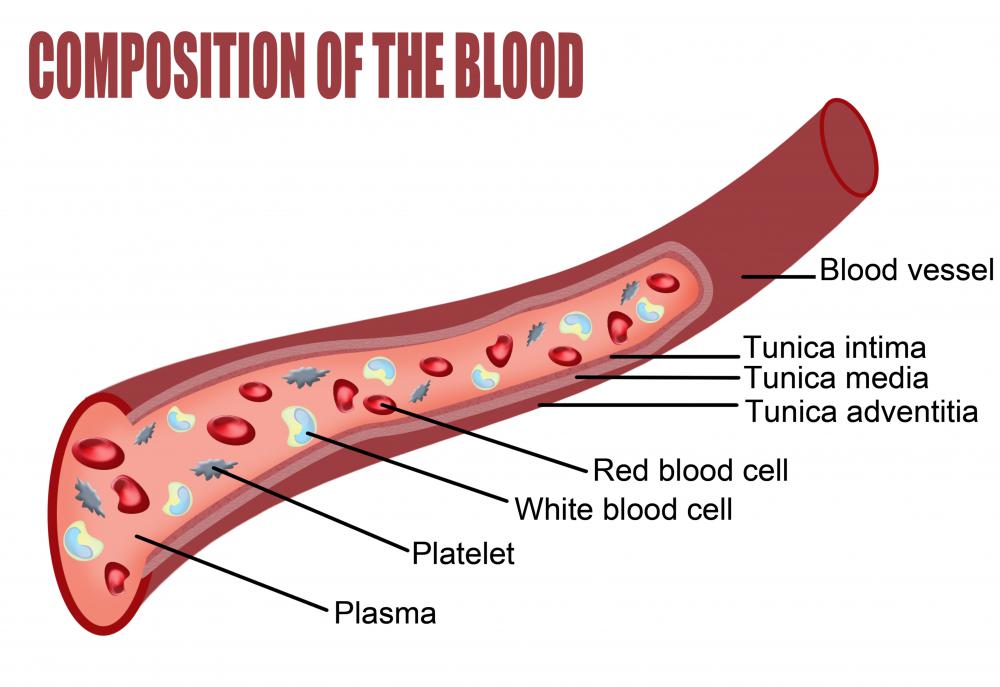
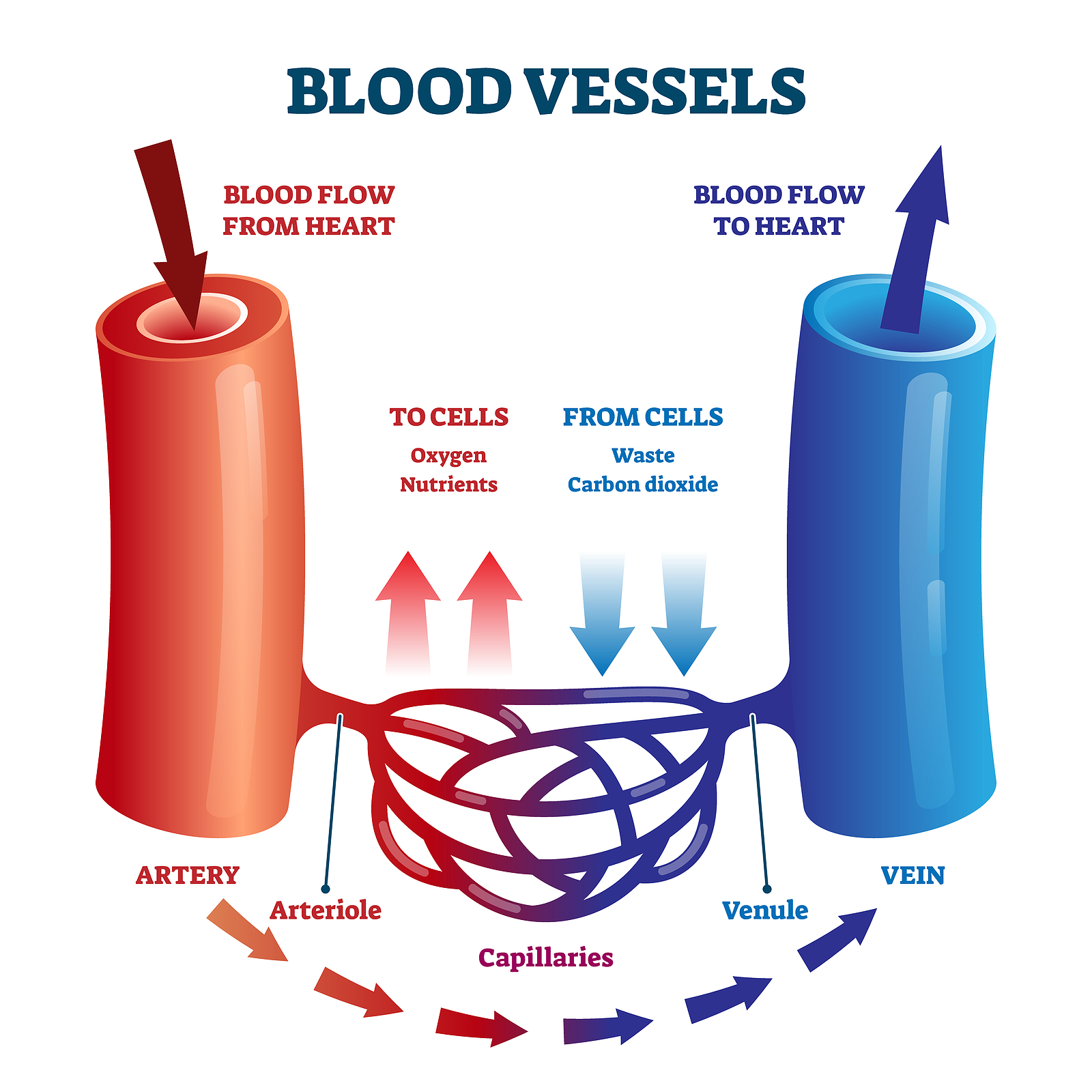
Drawing Of Blood Vessels - The circulatory system, also called cardiovascular system, is a vital organ system that delivers essential substances to all cells for basic functions to occur. Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels. New 3d rotate and zoom. Web blood vessels circulate blood throughout your body. By the end of this section, you will be able to: They receive blood directly from the heart and need to be elastic to accommodate the surge and contraction as blood. Additionally, other blood vessels return from these tissues with oxygen poor blood back to the heart. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web the great vessels of the heart include your aorta, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary veins and vena cava (superior and inferior). Blood is carried through the body via blood vessels. Distinguish between elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles on the basis of structure, location, and function. New 3d rotate and zoom. Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels. The chapter includes background information (section 2.1), practical guidance (section 2.2) and illustrations (section 2.3) relevant to best practices in phlebotomy. These layers surround. Blood vessels include veins, arteries and capillaries. Distinguish between elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles on the basis of structure, location, and function. Web describe the basic structure of a capillary bed, from the supplying metarteriole to the venule into which it drains. Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels. Web identify. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web describe the basic structure of a capillary bed, from the supplying metarteriole to the venule into which it drains. Blood vessels include veins, arteries and capillaries. They receive blood directly from the heart and need to be elastic to accommodate the surge and contraction as blood. The second. By the end of this section, you will be able to: They help deliver oxygen to vital organs and tissues, and also remove waste products. The tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. Web identify the vessels through which blood travels within the pulmonary circuit, beginning from the right ventricle of the heart and ending at the left. Web the most appropriate site to draw blood is selected based on vessel accessibility, patient age, and health status. Usually, the antecubital area, where the elbow bends, is used to access the. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web blood is carried through the body via blood vessels. Web describe the basic structure of a. Web learn all about the heart, blood vessels, and composition of blood itself with our 3d models and explanations of cardiovascular system anatomy and physiology. Web the right atrium and ventricle receive deoxygenated blood from systemic veins and pump it to the lungs, while the left atrium and ventricle receive oxygenated blood from the lungs and pump it to the. Web describe the basic structure of a capillary bed, from the supplying metarteriole to the venule into which it drains. Web blood vessels form the extensive networks by which blood leaves the heart to supply tissue. The first step in drawing blood correctly is to identify the appropriate veins to puncture. New 3d rotate and zoom. Compare and contrast the. The aorta and pulmonary arteries are the elastic arteries. Endothelial cells with a thin subendothelium of connective tissue and discontinuous elastic laminae. Distinguish between elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles on the basis of structure and location. Distinguish between elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles on the basis of structure, location, and function. The second image is titled cross section. The first step in drawing blood correctly is to identify the appropriate veins to puncture. The tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. Web blood vessels form the extensive networks by which blood leaves the heart to supply tissue. They connect directly to your heart and play a vital role in your circulatory system. For adult patients, the. Endothelial cells with a thin subendothelium of connective tissue and discontinuous elastic laminae. Web blood vessels circulate blood throughout your body. Compare and contrast veins, venules, and venous sinuses on the basis of structure, location, and function. New 3d rotate and zoom. Web learn all about the heart, blood vessels, and composition of blood itself with our 3d models and. Compare and contrast veins, venules, and venous sinuses on the basis of structure, location, and function. Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels. Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels. For adult patients, the most common and first choice is the median cubital vein in the antecubital fossa. Web there is a drawing of a tube labeled capillary (small blood vessel) and inside the tube there are disc shaped structures labeled red blood cell, erythrocyte. Web learn all about the heart, blood vessels, and composition of blood itself with our 3d models and explanations of cardiovascular system anatomy and physiology. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web blood is carried through the body via blood vessels. Discuss several factors affecting blood flow in the venous system. Distinguish between elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles on the basis of structure, location, and function. Compare and contrast the three tunics that make up the walls of most blood vessels. Web the right atrium and ventricle receive deoxygenated blood from systemic veins and pump it to the lungs, while the left atrium and ventricle receive oxygenated blood from the lungs and pump it to the systemic vessels which distribute it throughout the body. Web the most appropriate site to draw blood is selected based on vessel accessibility, patient age, and health status. Web the walls of most blood vessels have three distinct layers: The tunica externa, the tunica media, and the tunica intima. The aorta and pulmonary arteries are the elastic arteries.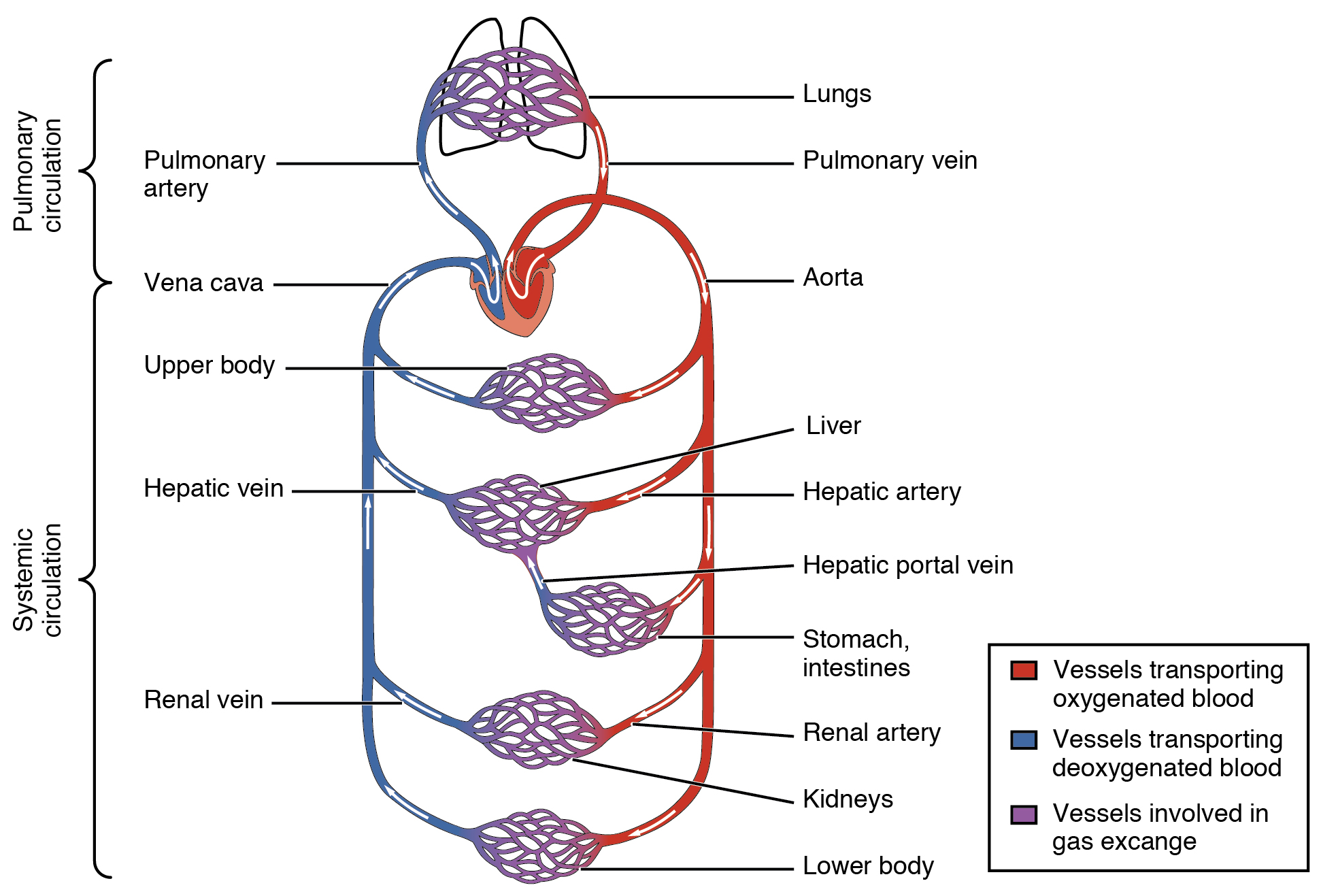
20.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels Anatomy and Physiology
Circulatory Blood Vessels

Structure and Function of Blood Vessels · Anatomy and Physiology
What are Blood Vessels? (with pictures)

What Are Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Facts DK Find Out
How blood flows through the body MooMooMath and Science
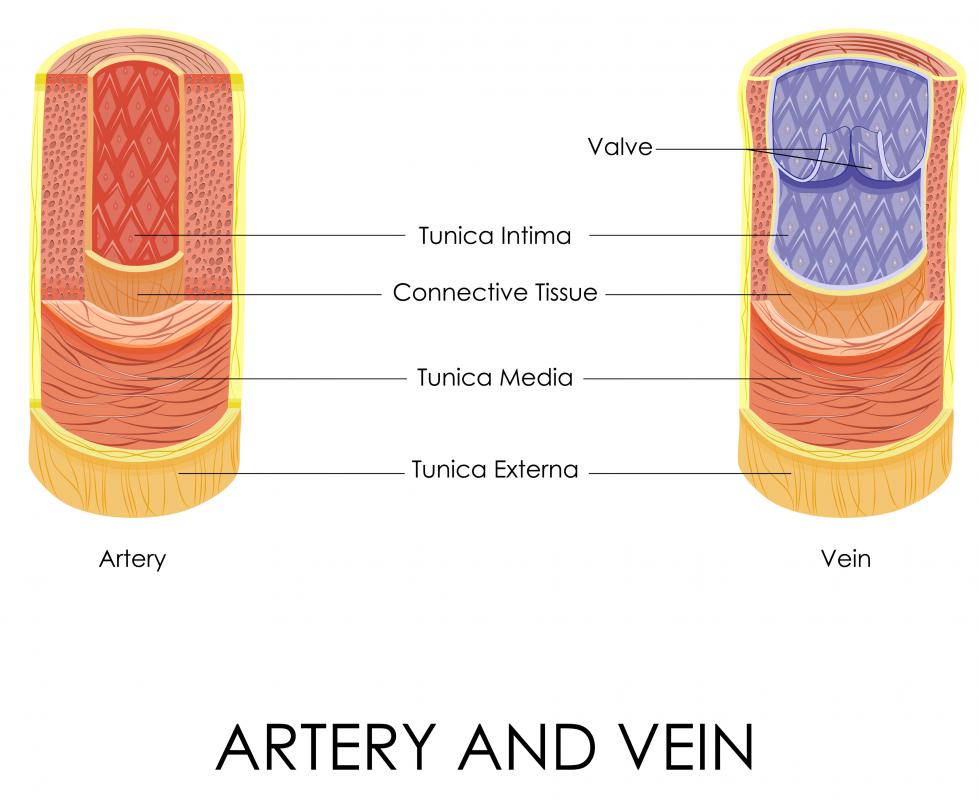
What are Blood Vessels? (with pictures)
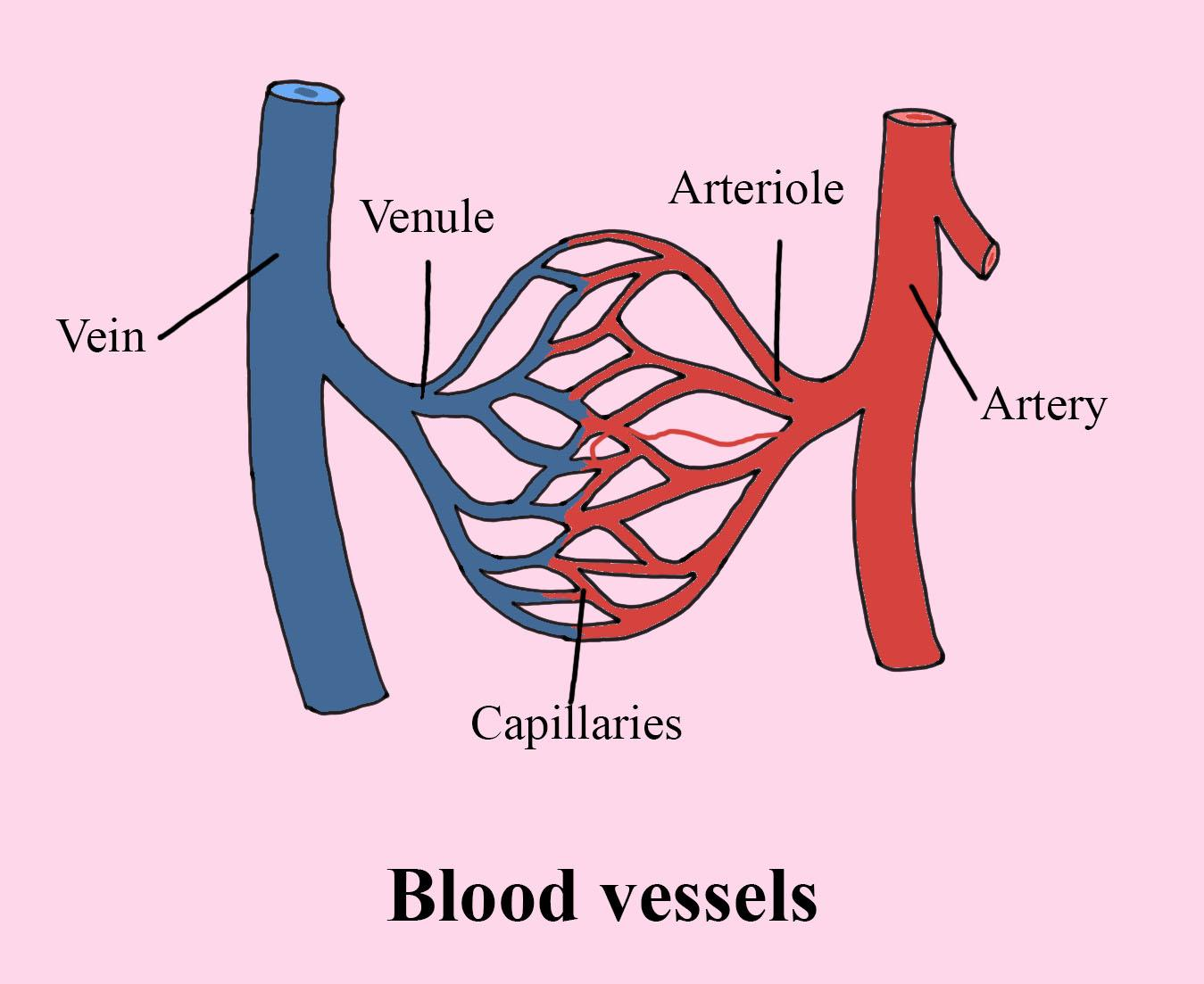
Blood Vessel Diagram Label
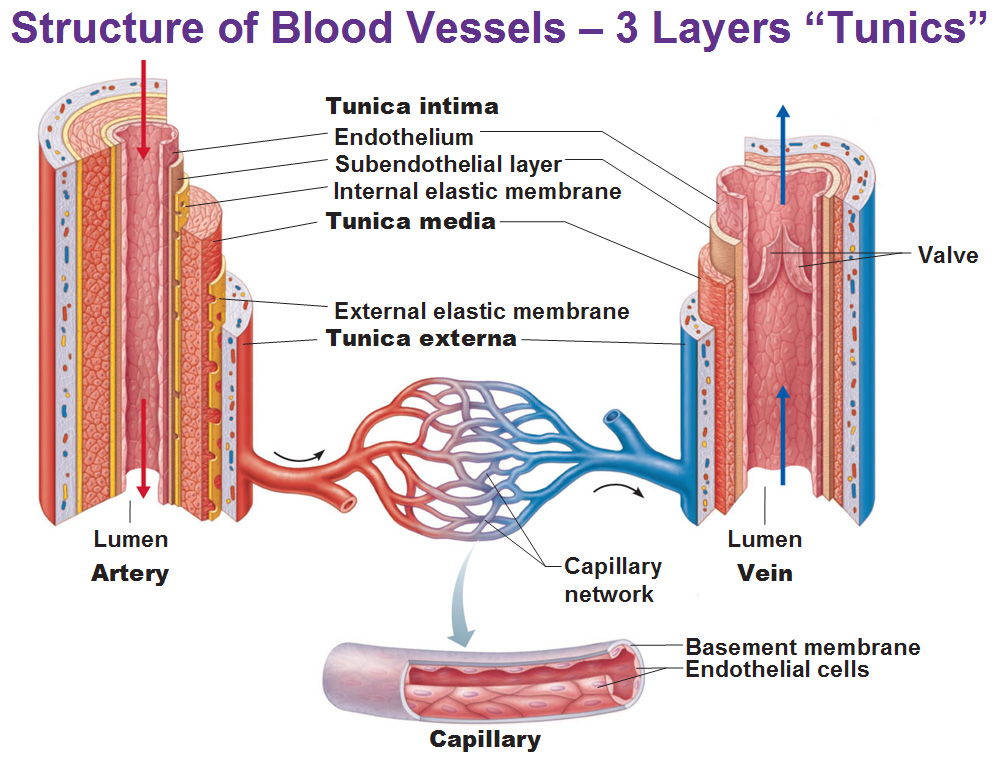
Blood vessels (Types, structure and functions) Online Science Notes

Blood vessel Definition, Anatomy, Function, & Types Britannica
Distinguish Between Elastic Arteries, Muscular Arteries, And Arterioles On The Basis Of Structure, Location, And Function.
Web Describe The Basic Structure Of A Capillary Bed, From The Supplying Metarteriole To The Venule Into Which It Drains.
By The End Of This Section, You Will Be Able To:
It Is The Thickest Part Of An Elastic Artery.
Related Post: