Draw The Ray Diagram
Draw The Ray Diagram - Properties of image formed in plane mirror. Linear magnification (m) concave mirror solved questions. A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. 260k views 6 years ago. Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. Web the location (and nature) of the image can be found by drawing a ray diagram: The smooth side is the reflecting part of the mirror, and the dotted side is the back. Draw reflected rays to the image. Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a real image will be formed, and the converging lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way: Use law of reflection to work out incident rays. A ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a. Which of the following diagrams shows the reflected ray correctly? For example, you can draw a ray of light parallel to the principal axis which reflects off the mirror and passes through the principal focus (like in this video). Web refraction ray diagrams: Web concave mirror ray diagrams. Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. Relation between radius of curvature and focal length. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. Web first, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. Properties of image formed in plane mirror. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Web the anatomy of a curved mirror. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Web a ray diagram is a. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature, distance of object and image. Web first, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. 260k views 6 years ago. Relation between radius of curvature and focal length. A ray of light is incident on a spherical mirror at the pole, p. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: Web explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. In this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for double. The two diagrams below show how to determine image location, size, orientation and type for situations in which the object is located at the center of curvature and when the object. Web once the method of drawing ray diagrams is practiced a couple of times, it becomes as natural as breathing. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and. Ray diagrams mirrors and different types of lenses. Web the location (and nature) of the image can be found by drawing a ray diagram: The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Where both reflected rays meet is point a' and the image formed is a'b' this image is formed between center. Web concave mirror ray diagrams. What is the path of the ray after it passes through the lens? Identify and mark the object distance. Web first, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. Which of the following diagrams shows the reflected ray correctly? Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a real image will be formed,. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. There are a few important things to note: Web ray diagrams for lenses. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. Web explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Web once the method of drawing ray diagrams is practiced a couple of times, it becomes as natural as breathing. A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. Diagram showing the formation of a real image by a lens. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. We draw another ray which passes through center of curvature. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. The smooth side is the reflecting part of the mirror, and the dotted side is the back. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Linear magnification (m) concave mirror solved questions.
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
How To Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT) PDF
---teachoo.png)
Convex Lens Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table Teachoo
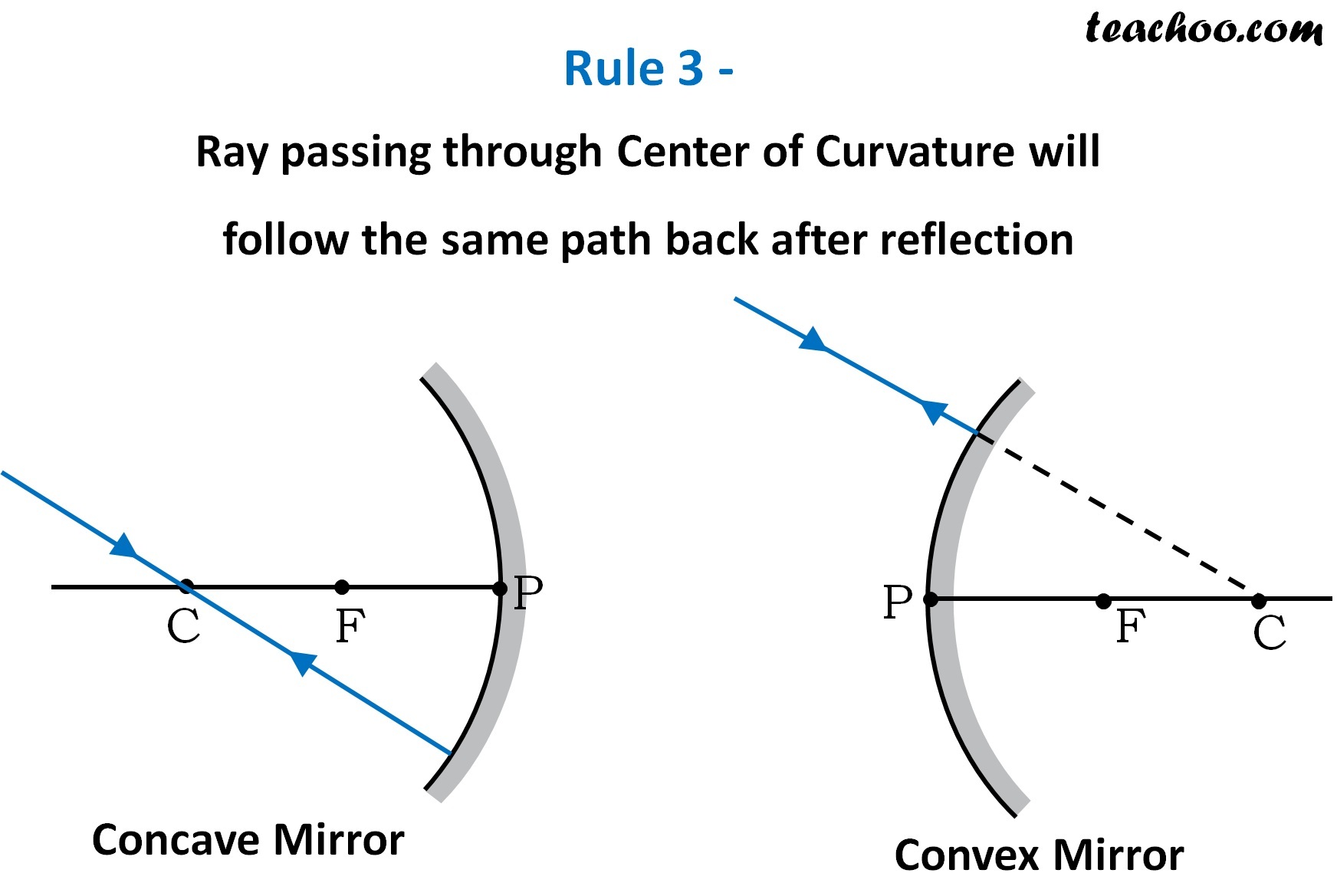
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
Ray diagrams for convex mirrors

How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10
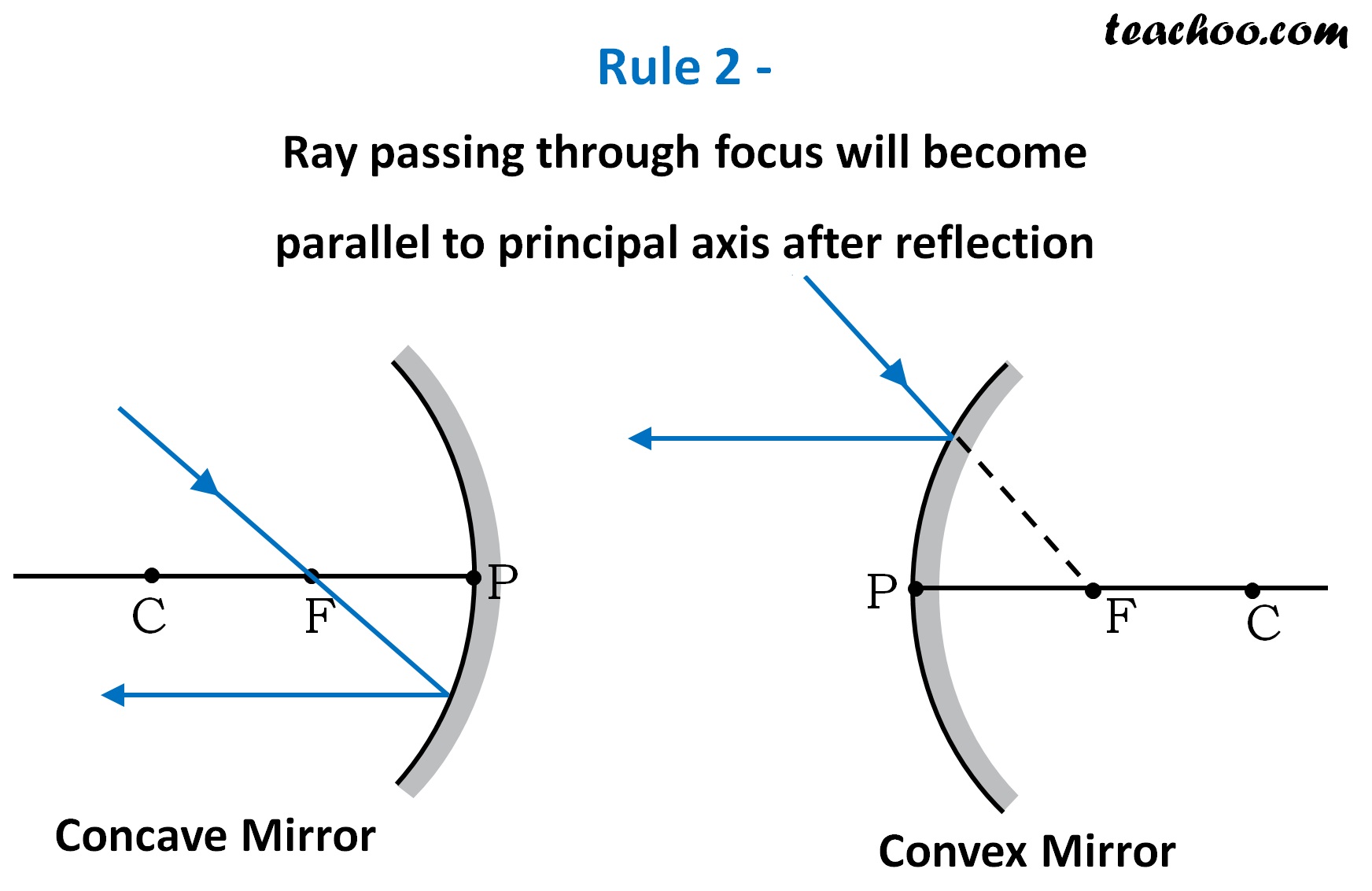
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
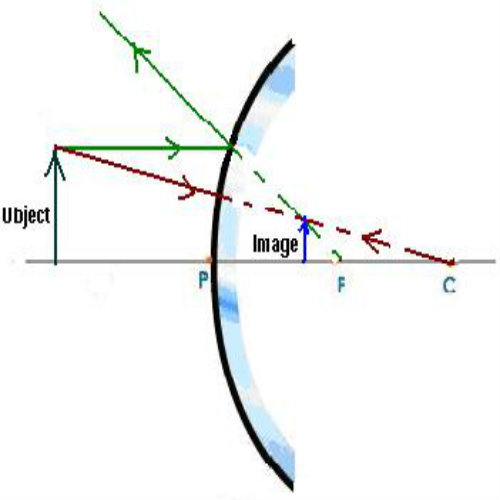
How to Draw a Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors
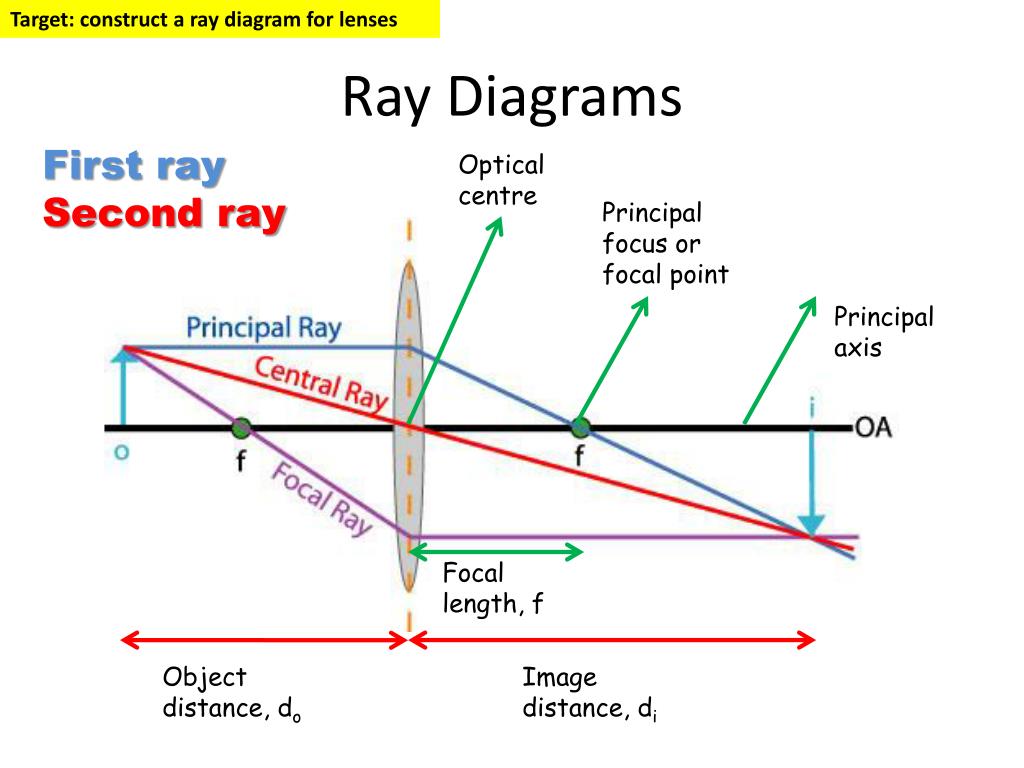
PPT Ray Diagrams PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6878954
A Ray Of Light Is Incident On A Spherical Mirror At The Pole, P.
Web In A Ray Diagram, You Draw Each Ray As:
Web Ray Diagrams Are Employed To Comprehend The Behaviour Of Light And Better Understand Image Formation.
What Is The Path Of The Ray After It Passes Through The Lens?
Related Post:

.PNG)