Draw The Base Thymine From Dna
Draw The Base Thymine From Dna - As you can see in figure1, the nucleotides only vary slightly, and only in the nitrogenous. You do not have to consider stereochemistry • you do not have to explicitly draw h atoms. Thymine (t) is one of the four nucleotide bases in dna, with the other three being adenine (a), cytosine (c) and guanine (g). Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) or cytosine (c). Web this is the basis for chargaff’s rule; Web the five bases that are found in nucleotides are often represented by their initial letter: Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a. • do not include lone pairs in your answer. Dna, along with rna (ribonucleic acid), regulates. Web the rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (a) in the dna of an organism, the amount of thymine (t) is the. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Thymine (t) is one of the four nucleotide bases in dna, with the other three being adenine (a), cytosine (c) and guanine (g). Web replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: What are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine? Namely, a. Narration one copy of the. Thymine (t) is one of the four nucleotide bases in dna, with the other three being adenine (a), cytosine (c) and guanine (g). In other words, adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and. Web the building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose. In other words, adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and. As you can see in figure1, the nucleotides only vary slightly, and only in the nitrogenous. Dna, along with rna (ribonucleic acid), regulates. Figure 7 each base specifically pairs with one other base adenine and. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Web the rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (a) in the dna of an organism, the amount of thymine (t) is the. Dna, along with rna (ribonucleic acid), regulates. Web replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle. Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while. Dna, along with rna (ribonucleic acid), regulates. Web a nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: Web the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: What are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine? Figure 7 each base specifically pairs with one other base adenine and. Web a nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while. Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) or cytosine (c). They will not be considered in the. What are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine? Draw the base thymine from dna. Web the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: Web the five bases that are found in nucleotides are often represented by their initial letter: Dna, along with rna (ribonucleic acid), regulates. Web thymine, organic compound of the pyrimidine family that is a constituent of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). Because of their complementarity, there is as much adenine as thymine in a dna molecule and as much guanine as cytosine. Web the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: Web the building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which. Web the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while. Web a nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: As you can see in figure1, the nucleotides only vary slightly, and only in. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. • do not include lone pairs in your answer. Web the rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (a) in the dna of an organism, the amount of thymine (t) is the. Web chemistry questions and answers. You do not have. Web the rules of base pairing explain the phenomenon that whatever the amount of adenine (a) in the dna of an organism, the amount of thymine (t) is the. Web the five bases that are found in nucleotides are often represented by their initial letter: Web thymine, organic compound of the pyrimidine family that is a constituent of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). Web this is the basis for chargaff’s rule; Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and cytosine (c) always. Web the building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: Draw the base thymine from dna. Web a nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: • do not include lone pairs in your answer. Figure 7 each base specifically pairs with one other base adenine and. What are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine? Dna, along with rna (ribonucleic acid), regulates. Adenine and thymine are bound to one another via two hydrogen bonds while. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. Web replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) or cytosine (c).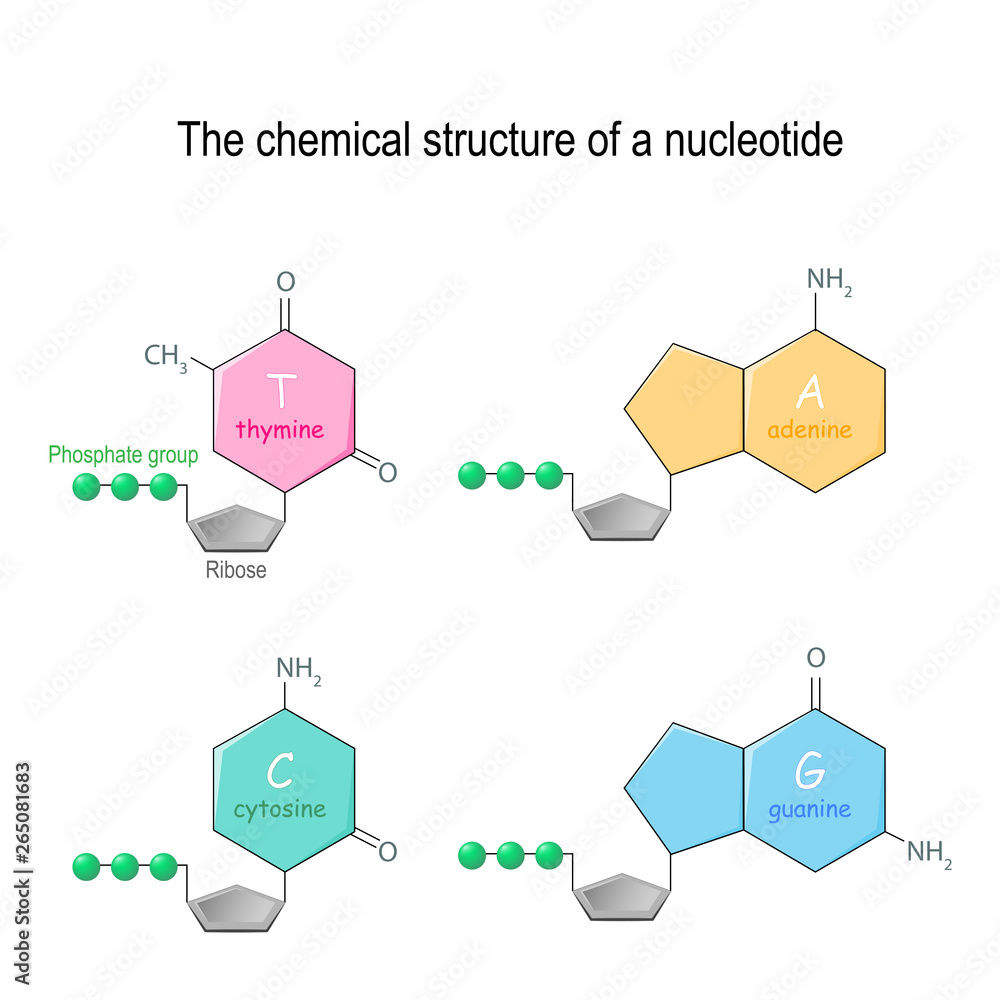
The chemical structure of a nucleotide. four main bases found in DNA

DNA structure including dinucleotide base pairs of adenine to thymine
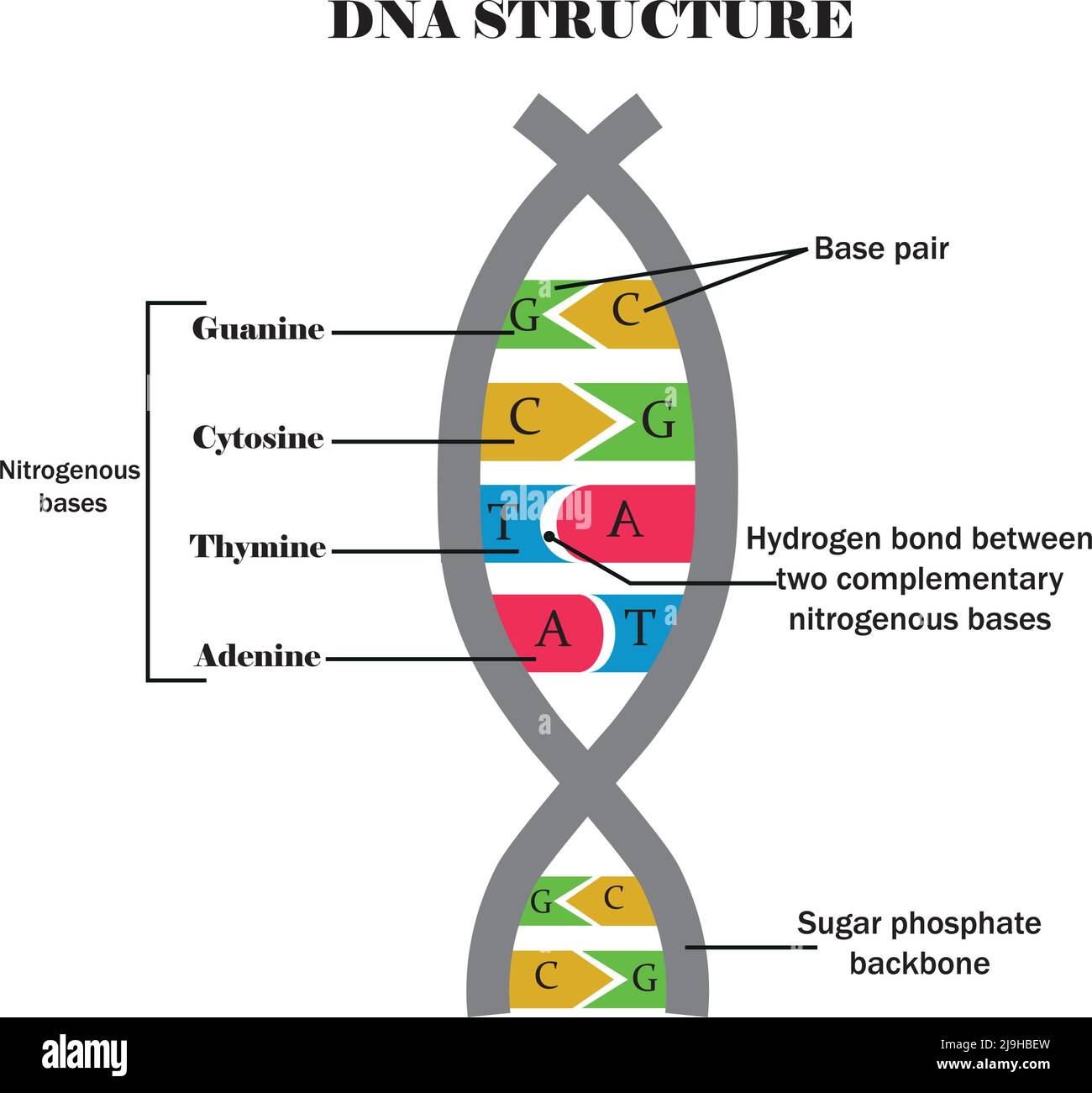
DNA structure.DNA with its components cytosine,guanine,adenine

19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and

Chemical Structural Formula And Model Of Thymine Stock Illustration

The Structure of DNA by Ron Vale

Cell Biology Glossary DNA Base Pairing ditki medical & biological
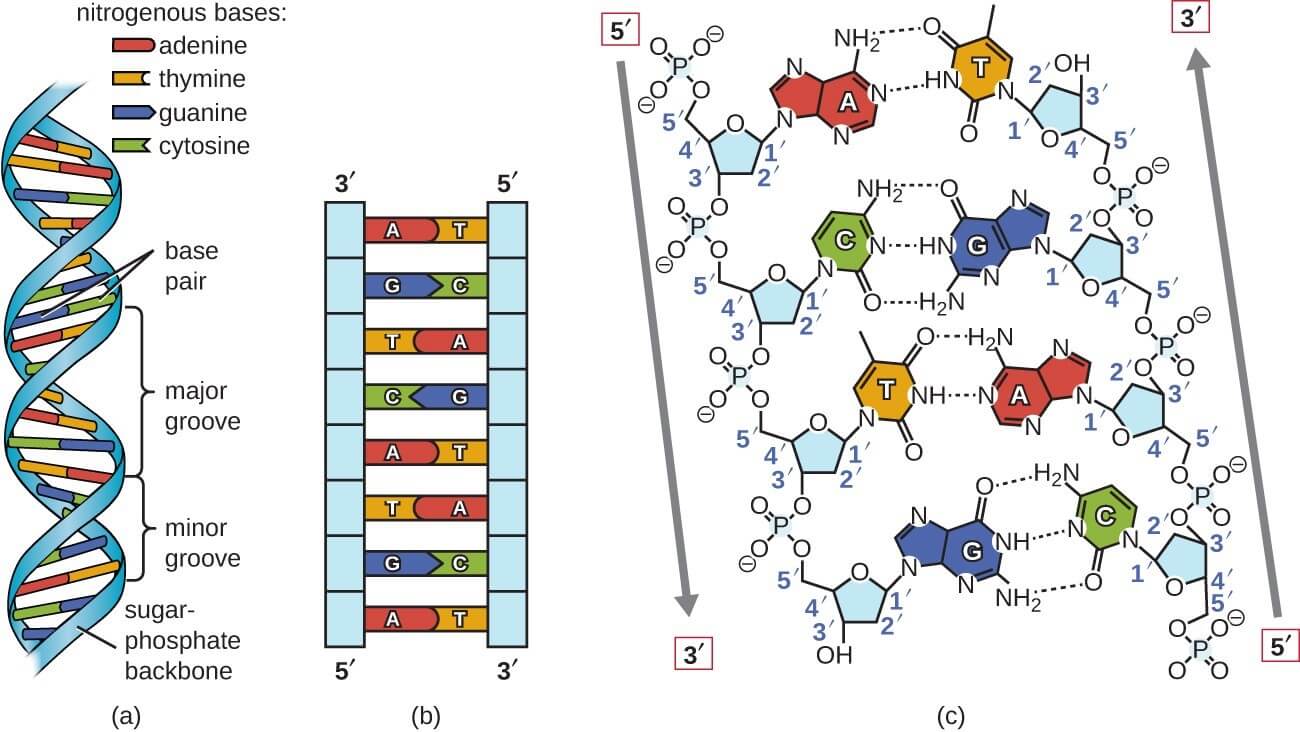
DNA Structure & Function A Simple Guide for Beginners
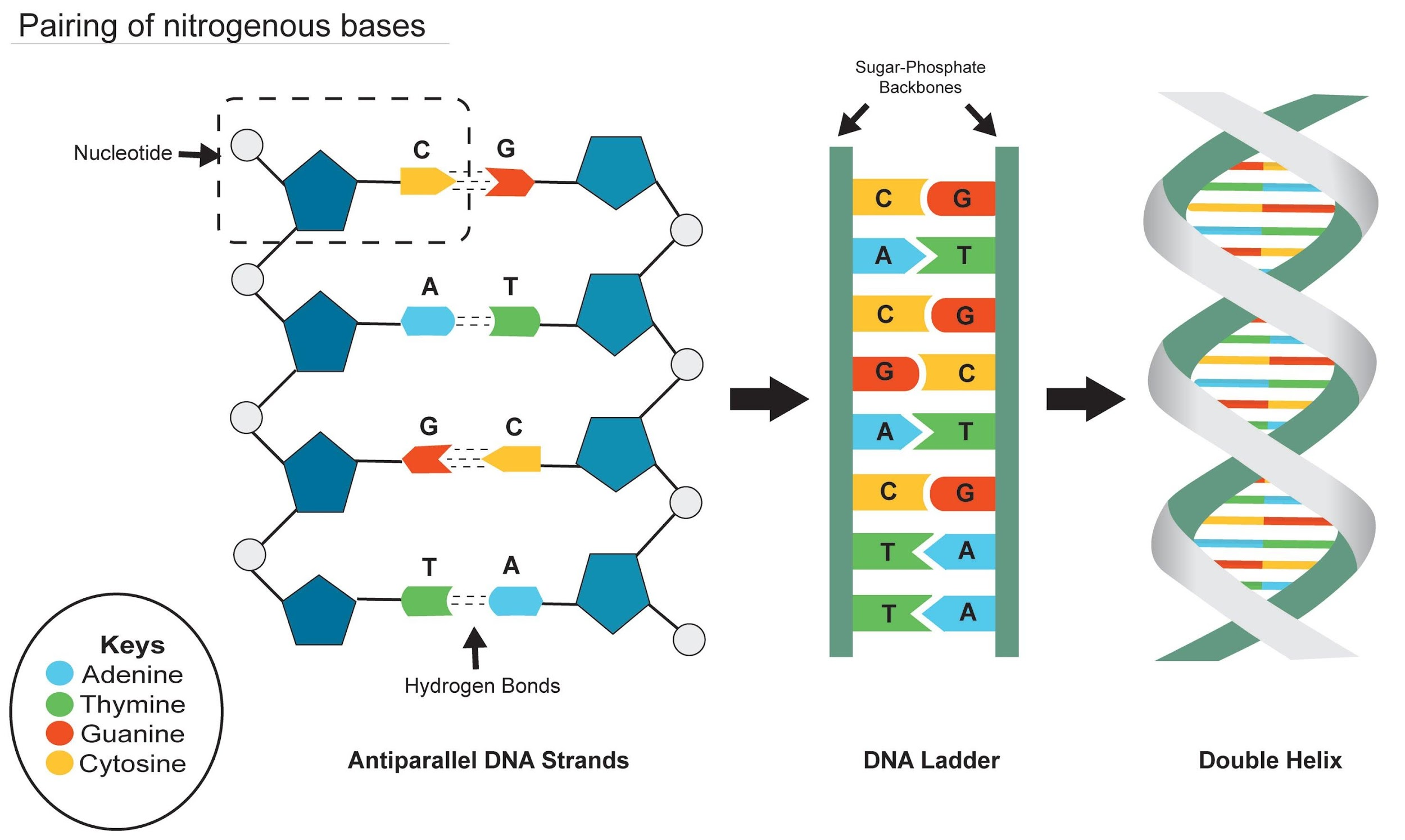
Adenine of DNA is equimolar with(a) Uridine(b) Thymine(c) Guanine(d
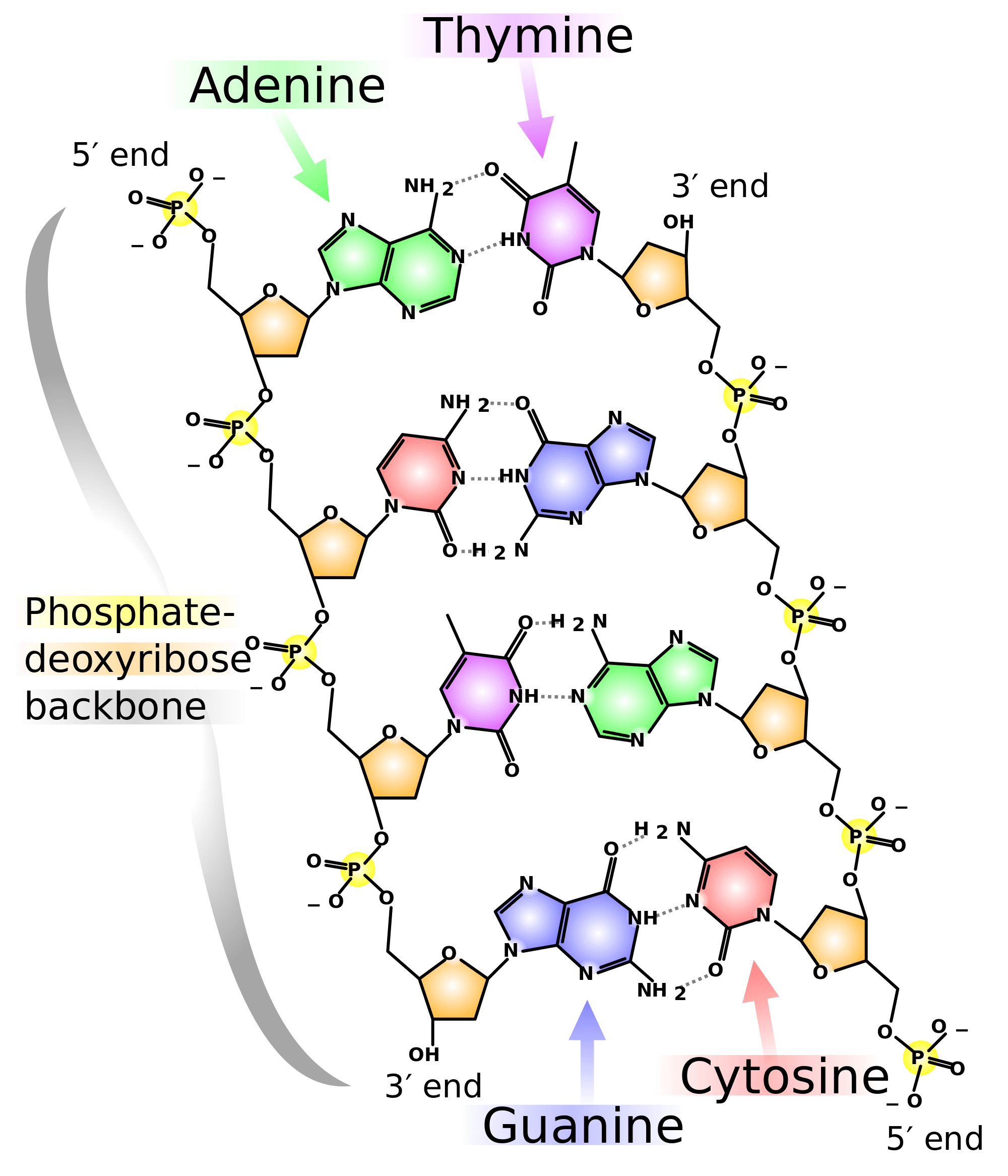
DNA Base Pairs — Overview & Structure Expii
Web Diagram Showing How Adenine And Thymine Base Pair While Guanine And Cytosine Base Pair.
Web The Four Bases In Dna Belong To Two Families Whose Numbering Systems Are Shown.
They Will Not Be Considered In The Grading.
Web Chemistry Questions And Answers.
Related Post: